
A Report from a compensation software company saw that about 60 percent out of the 1000 employed U.S. adults who were part of the survey were the ones who decided to switch companies for a more ideal one that implements the concept of pay transparency. As more organizations embrace such principles, understanding the different pay transparency laws across states in 2025 becomes ardently essential.
Understanding pay transparency, its advantages, and how to put it into practice is crucial as more states pass legislation requiring it. Like passing the Equal Pay Act which did lay the foundation to several other laws and other upcoming laws like the ones seen in Illinois wherein a new wage transparency law was signed.
Pay transparency is becoming an increasingly pivotal component of organizations in creating a positive work environment for employees, aiming to foster equality, fairness, and trust. So, this guide delves into the concept of pay transparency, the laws surrounding it, and how it benefits everyone within the organization.
Pay transparency is defined as a practice of openly sharing information regarding employee compensation, including salaries, benefits, and sometimes the criteria or processes behind pay decisions. This includes in it the detailed breakdowns of the compensation plan for an employee and also the general salary bands that are offered for their job roles.
Internal Pay Transparency: Employees within an organization have access to salary information for their colleagues or roles within the company.
External Pay Transparency: Companies disclose pay ranges or salary details in job postings or during recruitment processes, often required by law.
Laws requiring employers to disclose salaries to prospective hires and current workers are known as pay transparency laws. These regulations differ from one state to the next and may stipulate things like:
It is important to address structural inequalities like the gender wage gap, and these policies also seek to advance equality in all industries to ensure more compliance and strengthen the enforcement of pay transparency laws.
The evolution of these laws has been driven by advocacy for gender pay equity, workforce diversity, and economic justice. The key phases of the evolutionary network of laws that led to developments in pay transparency laws are -
The Equal Pay Act of 1963 in the US did attempt to primarily highlight the pay disparities in employment. However, transparency provisions were minimal, limiting enforcement.
States like California and New York introduced early pay transparency laws, protecting employees who discussed wages from employer retaliation.
Iceland (2018): Became the first country globally to have made pay equality mandatory, requiring companies to prove pay equity under government certification.
European Union countries began adopting other policies primarily requiring employers to disclose gender pay gaps in employment opportunities offered to employees, such as the Equality Act 2010.
Adopting pay transparency practices have its benefits within an organization for both employers and employees in several ways, such description of benefits include:
Employees appreciate openness and knowing their organization's pay structure are more likely to trust leadership, fostering a positive work environment and encouraging more loyalty for the company. So, ensuring such fair pay and salary transparency helps foster a level of trust and fairness within the organization.
Transparent pay policies help identify and address wage disparities which also helps in reducing wage gaps, promoting equity and inclusivity within the organization.
Job seekers are drawn to organizations that prioritize fairness and clarity in the compensation programs of an organization, highlighting how they respect the idea of pay equity among all, which creates a competitive advantage for them in the market.
Employees are less likely to leave when they perceive fairness in compensation, salaries and it also reduces the overall turnover costs as well.
There are specific regions that enforce certain laws on pay transparency and communication of the wide range of wage scale of maximum salary that also require companies to disclose certain salary information, or some have restrictions on such disclosure.
Employers equal to or more than 15 employees must most assuredly make sure to disclose the pay scales of what’s paid in the job postings even the remote jobs.
Salary information must clearly be shared with current employees upon the request of these employees. It also prohibits the employers from asking for salary history from the job applicants.
Salary and wage information must be shared with current employees upon request. Penalties up to $10,000 upon any violations regarding the same.
Employers with ≥100 employees must report median and mean hourly rates by demographic annually; the penalties of this add up to $200 per employee for non-compliance by any means.
The Colorado Equal Pay for Equal Work Act, which was effective January 1, 2021, mandates employers to disclose:
It includes salary or pay ranges, bonuses, and benefits in job postings. It also elaborates on notifying employees of promotion opportunities.
It mandates maintaining records of job descriptions and wage rates as well.
Connecticut's wage transparency law mandates that all the employers with at least one employee in the state disclose salary ranges to all the other job applicants for the company and other employees upon request.
This law also applies to remote workers or applicants from outside Connecticut seeking remote work opportunities. Any means of violations regarding this can result in compensatory and punitive damages
Employers with 50 or more workers are required by Hawaii law to include information about their wage ranges to the job applicants. It starts from January 1, 2024.
Internal transfers, promotions, and positions in the public sector decided by collective bargaining agreements are examples of exceptions.
Illinois amended its Equal Pay Act of 2003, that requires employers with about 15 or more employees to disclose salary ranges, benefit descriptions, and additional compensation details to all the employees.
If job postings are electronic, a link to pay and benefits information is permissible. The law also prohibits any inquiries of salary history of the employees, and any means of non-compliance asks for about $500 fine for the first violation, $2,500 for the second violation, and $10,000 for any other subsequent violations.
Equal Work Law obligates employers to meet the disclosure requirements like the different salary ranges in job postings of applicants.
The law also prohibits any inquiries of salary history of the employees, and any means of non-compliance asks for about $300 per violation and it can escalate to up to $600 for any other repeated violations.
Minnesota wage transparency law requires employers with 30 or more employees to disclose salary ranges, benefits and other compensation to the job applicants or as a response to the applications for employment beginning from January 1, 2025.
This law aims to extend to other third-party recruiters posting on behalf of Minnesota employers.
Employers are required by the wage transparency law in Nevada to provide pay or wage ranges to job candidates during interviews and to current workers looking for promotions or transfers.
Inquiries into an employee's past wages are also forbidden by law, and noncompliance can result in fines up to $5,000.
Employers employing four or more workers in New York, including employment agencies, are required to tell job seekers about the minimum and maximum salary or hourly compensation ranges before promoting or transferring personnel as of September 17, 2023.
For commission-based roles, only a disclosure of commission-pay is mandated. The law also prohibits any inquiries of salary history of the employees, and any means of non-compliance asks for about $1,000 for the first means of violation, $2,000 for the second violation, and $3,000 for other subsequent offenses.
Rhode Island’s wage transparency statute mandates employers to give wage ranges for roles upon request from applicants or current employees.
The penalty for any kind of initial violation can roughly be $1,000 for the first infraction, $2,500 for a second within five years, and $5,000 for several infractions over a seven-year period.
In Washington State it requires full disclosure of wages, different benefits available to the employees, and additional compensation in job postings. It also applies to employers hiring Washington-based employees, including remote roles.
There are further advances that are expected in the year 2025 for different transparency laws. Since there is an increased focus on accountability in employees in organizations today. Key developments include -
Maryland’s Pay Transparency Law emphasizes on requiring prospective employees to disclose the different range of compensation, other salary ranges, benefits and additional compensation in the job postings for applicants. Compliance records of this need to be mentioned for 3 years and have penalties for non-compliance.
Companies or other private employers with 15 or more employees in Illinois must make sure that there are more transparency requirements of salary compensation, and make sure that they disclose their pay scales and other benefits for the employees to know.
This includes even job roles that are in Illinois or supervised from offices in Illinois. Internal promotion opportunities are offered by employers before posting externally.
These states already mandate more detailed salary disclosures in advertisements for potential employees and their legislation is more ready to inspire in other states as well in the year 2025.
Particular states like Kentucky and Maine are aiming to explore new salary disclosure laws as well. Indiana is reviving discussions on other pay equity legislation. This helps reduce any means of wage gaps and ensure more equal pay.
In the US, several states like California, Colorado, and New York require employers to disclose salary ranges in job postings, during interviews, or upon request. These laws vary by state, as some states have particular conditions to having such salary disclosures.
The EU’s Pay Transparency Directive, effective 2024, aims to ensure equal pay by requiring salary transparency in job ads and empowering employees to request pay information to address pay gaps.
Yes, Connecticut requires employers to provide wage ranges in job postings, during hiring, or when requested by employees.
Since Pay Transparency acts as one step closer towards bridging the pay gap, it is rather important to note that there are complexities and challenges that must be dealt with by careful planning and managing these transparent pay practices effectively in compensation packages and the considering the different forms of compensation and through compliance of the state’s Pay Transparency Laws as well. It also helps address issues like wage discrimination compelling compliance of such laws.
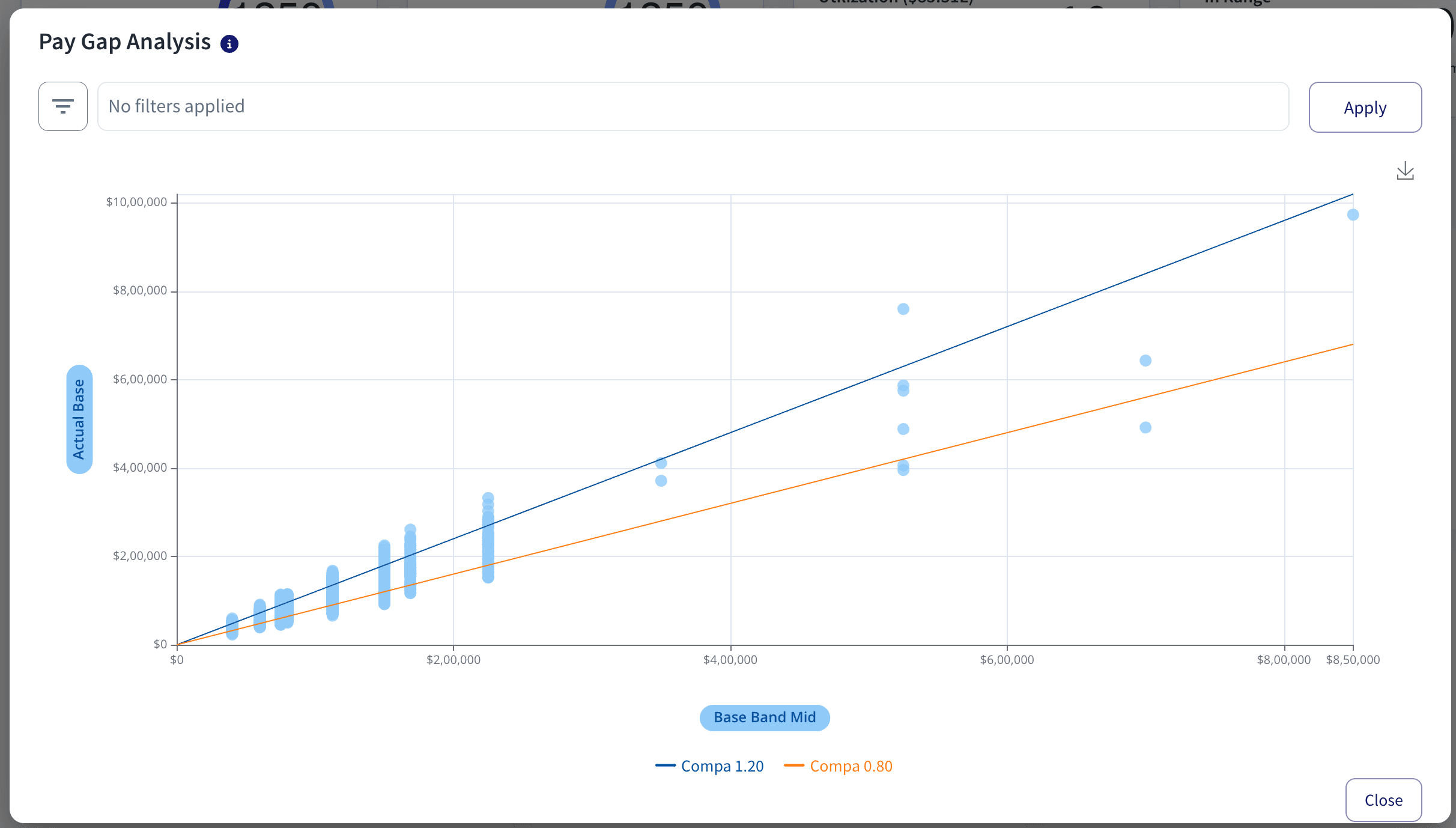
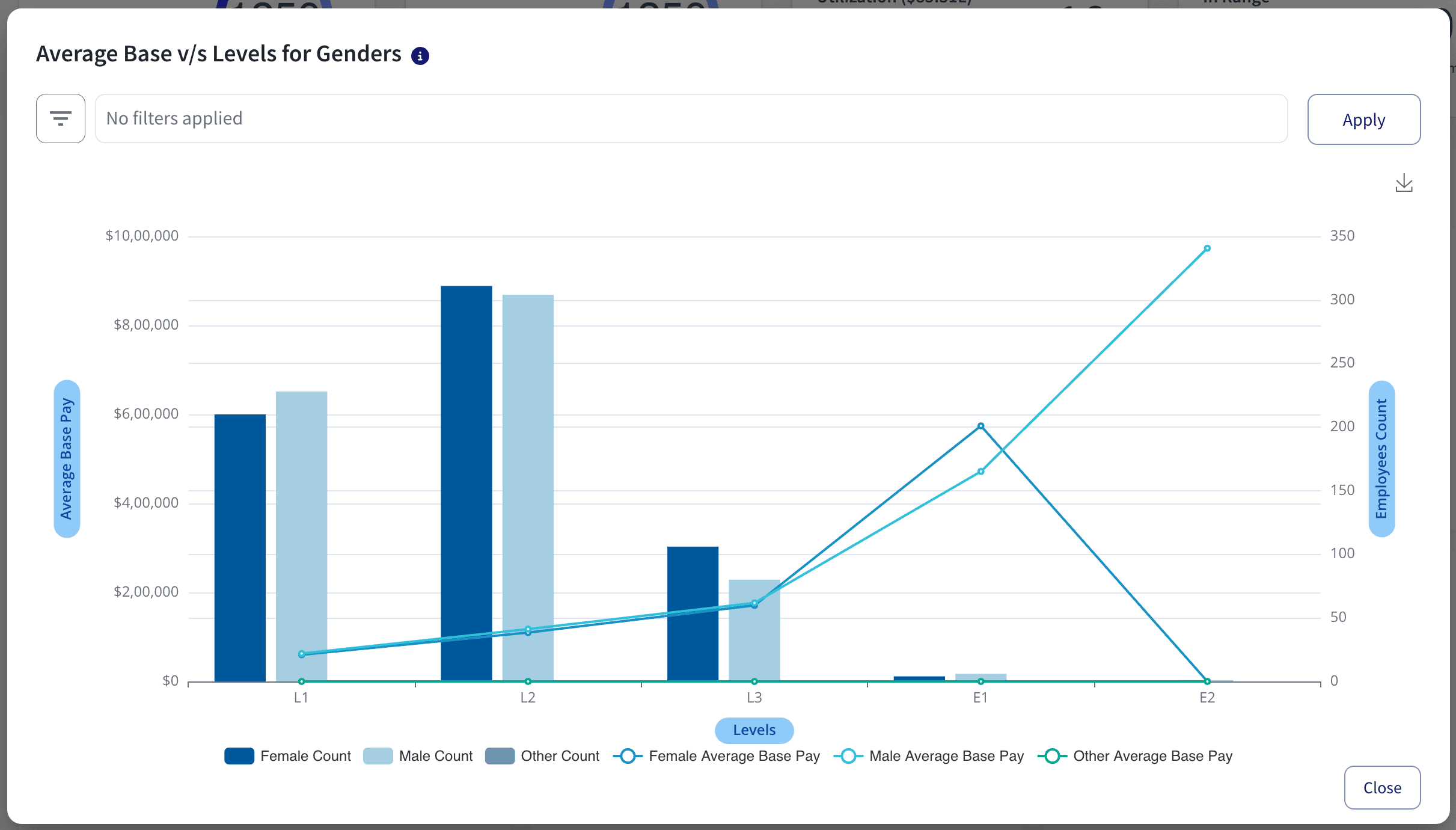
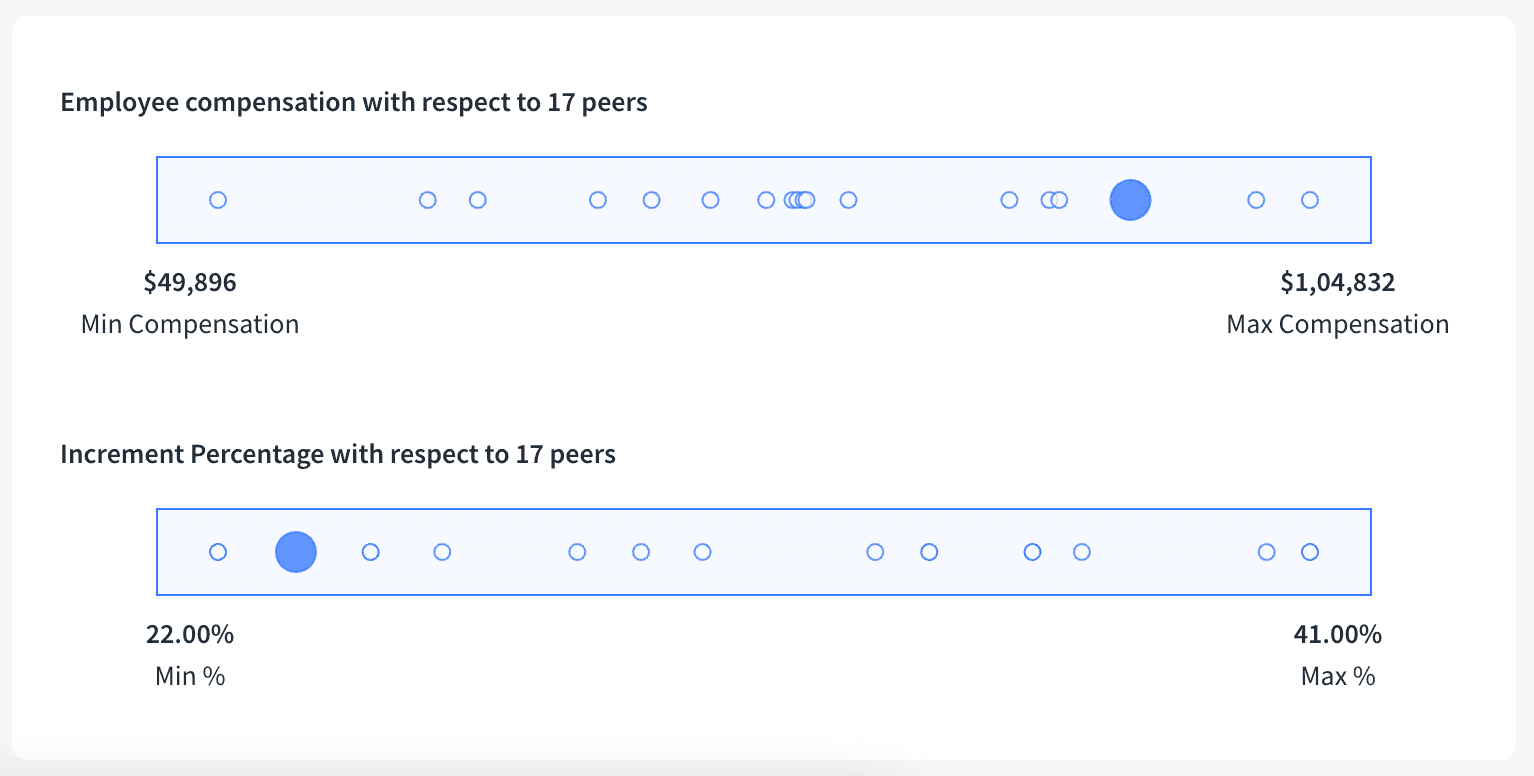
Pay transparency is becoming an ardent necessity as a concept within an organization. So, by being able to get a more open and structured approach to the compensation of an employee, this will also help companies instill trust and loyalty in the hearts of the employees.
Try the platform today to understand how CompUp can help you make data-driven and ensure transparency in your payment structure.
Revolutionizing Pay Strategies: Don't Miss Our Latest Blogs on Compensation Benchmarking