
When we talk about fair pay, does it always mean equal pay for the same role? If your answer is affirmative, then think again. What about those employees who put in more effort, bring more experience to the table, and drive the results better than others? This is where the pay-for-performance or PFP (or P4P) model shines.
This model ties compensation directly to employee performance. As per a survey published by the Harvard Business Review, 81% of high-performing companies implemented pay-for-performance practices, in contrast to 74% of average companies. But is this approach always the best option? Let’s take a closer look at what PFP is, how it works, and whether it’s the right fit for your organization.
At its core, the Pay-for-Performance (PFP) model links compensation to individual or team performance. This could mean offering higher pay or bonuses to employees who meet or exceed performance goals and, in some cases, reducing pay for those who don’t.
Unlike traditional compensation systems, where employees typically receive the same salary regardless of performance, PFP is designed to reward high achievers and motivate others to perform better. The idea is to align employee objectives with the organization's goals and encourage continuous improvement. Let’s understand how it’s different from a traditional compensation model.
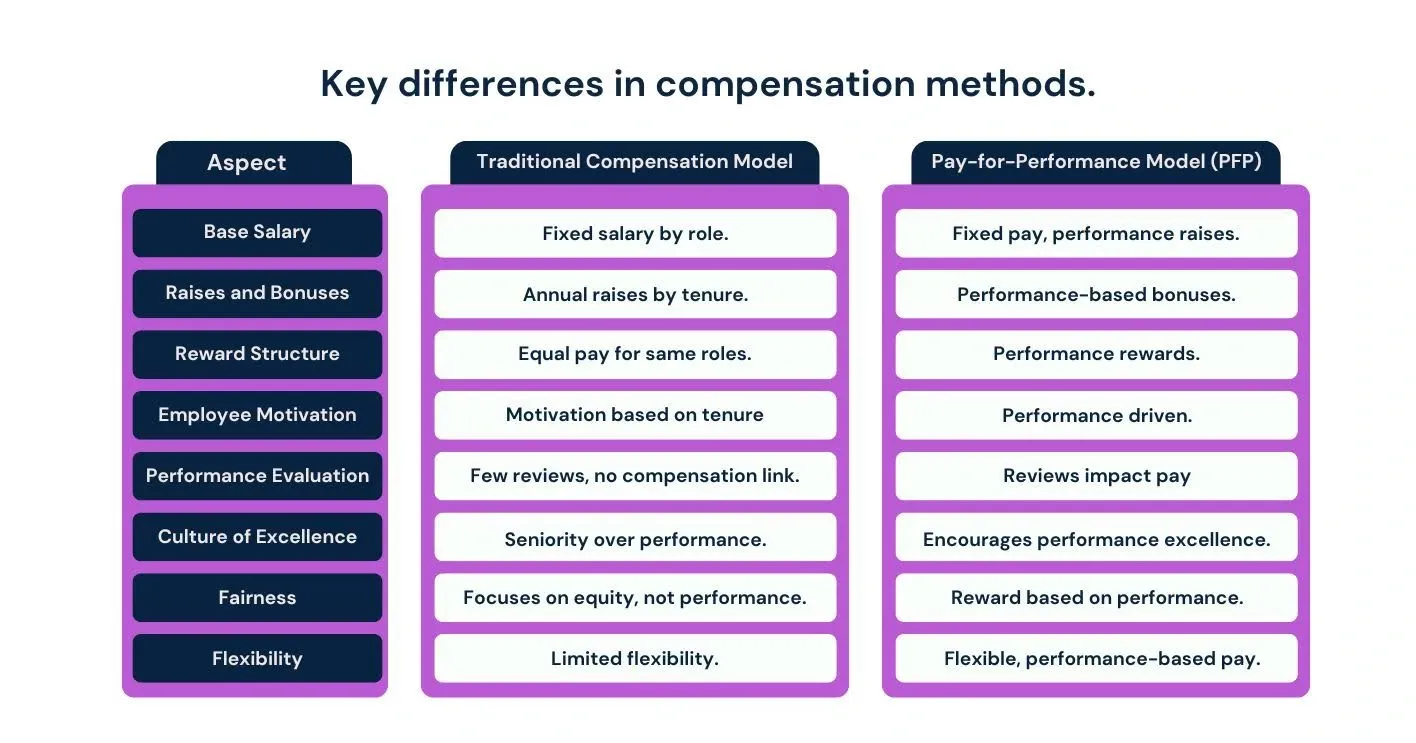
Compensation strategies play a crucial role in shaping an organization's culture and driving employee performance. Traditional compensation models and the PFP model offer different ways to reward employees for their contributions. While both aim to provide fair and competitive pay, they differ significantly in their approach to motivating employees and aligning compensation with company goals.
Now that you have a fair idea of how PFP models are different from traditional compensation models, let’s see why organizations choose the former.
Organizations adopt the PFP model for several reasons, primarily to increase motivation, align goals, and foster a high-performance culture. Here’s why many companies choose to implement this model:
PFP ties compensation directly to performance, offering employees a clear incentive to work hard and exceed expectations. Knowing that their efforts will result in tangible rewards motivates employees to stay engaged and productive.
PFP helps align individual goals with company objectives. When employees know their success contributes to the organization’s success, they are more likely to focus on achieving shared goals, leading to better overall performance.
A performance-driven compensation structure attracts high performers who are motivated by the opportunity to earn more based on their results, making it an attractive option for top-tier candidates.
PFP fosters a culture of excellence by rewarding employees who consistently perform well. It motivates the employees to strive for the highest standards, which boosts overall organizational performance.
Rather than offering the same pay for everyone, PFP ensures that high performers are rewarded for their contributions. This helps distinguish top talent and recognize their value to the organization.
With PFP, employees are accountable for their performance since their compensation is directly linked to results. This increases personal responsibility and ensures employees are motivated to meet or exceed expectations.
PFP provides employers with a way to control labor costs, as compensation is tied to performance. This ensures that pay increases or bonuses align with actual contributions, helping businesses maintain financial efficiency.
Companies can retain top talent by offering performance-based rewards. Employees who feel their hard work is recognized and rewarded are less likely to leave for other opportunities.
The benefits of opting for a PFP model seem convincing enough for you to consider it. If you’re thinking about implementing it, let’s take a look at the types of PFP models.
PFP models offer a range of options that can be tailored to different organizational needs. Below, we explore two of the most common types of PFP models: Merit Pay and Variable Pay, each with its own unique benefits and applications.
Merit pay is a salary increase awarded based on an employee’s performance over a given period. These raises are typically given during annual salary reviews and are directly linked to the individual’s performance against pre-set goals or performance criteria. The better the performance, the greater the raise.
This model encourages employees to continuously improve and achieve higher performance standards year after year, as their efforts are directly rewarded with salary increases. Merit pay is often structured to be progressive, meaning that the better the employee's performance, the more significant the salary increase they can expect. However, merit pay works best when the company has clear performance metrics and a transparent evaluation process.
Example: An employee who exceeds sales targets by 15% may receive a 10% raise, while an employee who meets expectations might receive a 5% raise.
Variable pay includes bonuses, commissions, and other incentives that are not guaranteed but awarded based on performance metrics. Its core feature is flexibility, as it can be adjusted based on an employee's contribution to short-term goals or exceptional achievements.
There are several types of variable pay, including:
Variable pay allows organizations to reward employees for short-term goals and exceptional efforts. Unlike merit pay, which is usually based on an annual cycle, variable pay can be more frequent and focused on specific achievements, making it a versatile tool for incentivizing performance.
Example: A project manager who successfully completes a major client project ahead of schedule might receive a project bonus, while a salesperson who secures a large contract could be awarded a spot bonus.
Next up is the implementation of the PFP model. Let’s understand the intricacies of getting the PFP model into effect for your company.
Implementing a PFP system requires meticulous planning and consideration to make sure it aligns with organizational goals and is executed effectively. There are various key factors that play a vital role in the effective adoption and operation of a PFP system. Let’s explore these factors in more detail.
Before implementing a PFP system, assess the company’s financial situation and strategic goals. Ensure the budget allocated for performance-based rewards is sustainable and aligns with the company’s objectives. The rewards should motivate employees without overextending financial resources.
A solid performance management system is essential for PFP to work effectively. Clear performance metrics, regular reviews, and ongoing feedback help ensure employees understand how their work is evaluated and rewarded, promoting fairness and transparency in the system.
Successful implementation requires consistency, transparency, and clear communication. Employees must understand how their performance will be measured, how rewards are determined, and that the system is applied fairly across the board. Open communication builds trust and ensures the system's acceptance.
If you’re almost convinced to implement a PFP model, let’s take a closer look at the pros and cons.
The PFP model has several notable advantages, but it also comes with potential challenges. Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons to consider when adopting this compensation approach.

Still thinking if PFP is the best approach for your company? Let us solve it for you. Here’s how it affects individual and organizational growth.
The Pay-for-Performance (PFP) model can be highly effective in driving positive outcomes within an organization. Let’s explore the key areas of its effectiveness:
As mentioned earlier, PFP boosts motivation by directly linking pay to performance. When employees are informed that their efforts will be rewarded, they are more likely to be engaged and productive. This clear connection between effort and reward encourages employees to put in extra effort and exceed expectations.
PFP encourages employees to seek professional development opportunities to improve their performance. Knowing that their growth will lead to greater rewards, employees are motivated to continuously improve their skills and knowledge, benefiting both themselves and the organization.
A well-executed PFP system can improve employee satisfaction and increase retention rates. When employees feel their contributions are fairly rewarded, they are more likely to stay with the company, reducing turnover and building a loyal workforce.
PFP aligns individual performance with the company’s strategic objectives. By linking compensation to company goals, employees are more focused on contributing to the organization’s success, ensuring that both individual and corporate growth go hand in hand.
Clear communication is crucial for PFP success. Employees must understand the performance metrics and how their results impact their rewards. Transparency in the system ensures that expectations are clear, increasing trust and motivation within the workforce.
Before we wrap up, here are some recommendations for implementing the PFP model effectively in your company.
Implementing a PFP model can be a powerful way to motivate employees, but its success depends on careful execution. Here are several key tips to ensure the system works effectively:
For a PFP system to be successful, the application of performance metrics and rewards must be consistent. Employees should clearly comprehend how their performance is being evaluated and how their efforts will be rewarded. The rules for praise should apply equally to everyone in similar roles, ensuring that rewards are based on objective criteria. Consistency in using the system helps avoid confusion and feelings of unfairness, creating a more engaged and motivated workforce.
Communication is key to ensuring the success of a PFP system. Employees need to know exactly how the performance evaluation works, what targets they need to hit, and how those targets relate to their rewards. Transparency in how performance is measured and how rewards are distributed builds trust in the system, helps manage expectations, and ensures that employees feel their efforts are being fairly evaluated.
A one-size-fits-all approach to PFP rarely works, as different roles have varying responsibilities and challenges. It’s important to customize the compensation strategies to align with the specific needs of each role or team. For example, a sales team might be rewarded based on revenue targets, while customer service teams could be evaluated based on customer satisfaction metrics. Customizing the PFP system ensures that the right behaviors are incentivized in a way that makes sense for each department.
For a PFP system to be effective, the goals set for employees must be clear, measurable, and achievable. Setting unrealistic or vague expectations can demotivate employees. By providing specific, attainable goals, employees have a clear path to follow and can easily track their progress. This helps maintain focus and keeps performance aligned with organizational objectives.
A PFP system should not be static. It’s essential to scrutinize its effectiveness and make adjustments as necessary. Regularly reviewing the system ensures that it continues to meet the needs of both the company and its employees. If certain metrics aren’t driving the desired outcomes or if employees express concerns, the system should be revised to reflect new priorities or challenges.
And there you have it! All you need to know about a Pay-for-Performance (PFP) model. It offers significant benefits, from boosting employee motivation and aligning personal goals with organizational objectives to fostering a high-performance culture. However, its success depends on careful planning, clear communication, and customization to suit your business's unique needs.
At CompUp, we specialize in developing customized PFP systems that align with your company’s goals, ensuring fair and transparent compensation practices that drive performance and engagement across all teams.
We help define clear performance metrics, tailor strategies for different roles, and provide ongoing support to refine and optimize the system over time. With CompUp, you can build a performance-driven culture that rewards excellence and supports business growth.
Ready to take your compensation strategy to the next level? Contact us today for a consultation or book a demo!
1. What is the Pay-for-Performance (PFP) model?
The Pay-for-Performance model ties compensation directly to individual or team performance, rewarding employees who meet or exceed goals and, in some cases, reducing pay for those who don’t. It aims to motivate employees and align their objectives with company goals.
2. What are the key differences between traditional compensation and Pay-for-Performance?
Unlike traditional compensation, where employees receive fixed salaries regardless of performance, PFP rewards employees based on their performance. This creates a more dynamic and performance-driven compensation structure, with the potential for raises and bonuses linked to achievements.
3. Why do companies use Pay-for-Performance models?
Companies adopt PFP models to boost employee motivation, align individual goals with company objectives, attract top talent, foster a high-performance culture, and control labor costs by rewarding actual performance rather than tenure.
4. What types of Pay-for-Performance models are there?
The two main types of PFP models are merit pay, which ties salary increases to performance over time, and variable pay, which includes bonuses and incentives awarded based on specific achievements or performance metrics.
5. How can I implement a Pay-for-Performance model successfully?
Successful implementation requires clear communication, consistency in applying performance metrics, and customized goals for different roles. Regular monitoring, transparency in reward distribution, and adjusting the system as needed are crucial for maintaining its effectiveness.

Customer Success Manager
Driven with the aim of becoming a valuable subject matter expert in the world of Total Rewards to be able to deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Revolutionizing Pay Strategies: Don't Miss Our Latest Blogs on Compensation Benchmarking