
Managing human resources efficiently is a growing challenge for many organizations. With outdated systems and manual processes, HR teams often struggle to stay organized and make informed decisions. Companies spend an average of 15 weeks selecting an HRIS, highlighting the importance of choosing the right system for smooth operations and strategic success.
The HR software market is projected to grow to $33.57 billion by 2028, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 10%. This growth reflects the increasing demand for tools like Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) for improving HR functions.
In this blog, we will explain what an HRIS is, how it works, and why it’s essential for modern HR management.
A Human Resource Information System (HRIS) is a software solution designed to efficiently manage and streamline HR functions. It centralizes employee data, automates routine tasks, and provides tools for payroll, benefits administration, recruitment, performance tracking, and more.
With an HRIS, you can consolidate disparate HR processes into one platform, eliminating manual errors and reducing administrative workload. It serves as a single source of truth for employee information, ensuring data accuracy and accessibility.
By digitizing HR operations, HRIS enables faster decision-making and supports compliance with labor regulations. HRIS lets you manage your workforce efficiently, freeing up time to focus on strategic initiatives that drive organizational growth.
Now, let’s examine the five main types of HRIS systems, offering insights into their specific capabilities and use cases.
Suggested Read: Top PayScale Alternatives and Competitors in 2025
HRIS systems are designed to automate and integrate various human resource functions within an organization. Understanding the different types of HRIS systems is essential for selecting the right solution based on your organization's operational complexity, size, and strategic objectives.
HRIS systems can be classified into five main types, each serving different levels of organizational needs. These include:
Operational HRIS systems are designed to handle basic HR tasks such as payroll, attendance, and employee data management. These systems focus on efficiency and day-to-day operations, making them ideal for smaller businesses or those with simpler HR needs.
These systems go beyond operational tasks, incorporating tools for performance management, recruitment, and benefits administration. Tactical HRIS solutions are suited for organizations looking to improve employee engagement and refine their HR functions.
This type of system focuses on aligning HR functions with organizational goals. It includes advanced analytics, workforce planning, and talent management features to help HR leaders make data-driven decisions that support long-term business strategies.
A more focused system designed to handle one or two specific HR functions, such as time tracking or benefits administration. Limited-function HRIS is best for companies that only need to manage certain aspects of HR without investing in a full-scale system.
A fully integrated system that covers all HR functions, from recruitment and onboarding to performance management and compensation planning. Comprehensive HRIS systems are ideal for large organizations that need a unified platform to manage all aspects of human resources.
The right HRIS system will grow with your business, providing the scalability and flexibility needed to meet both present and future HR demands.
Now that we have explored the various types of HRIS systems, it’s important to understand how they differ from other related HR software solutions. While HRIS, HRMS, and HCM all serve similar purposes, they have distinct features and functions.
Understanding the differences between HRIS, HRMS, and HCM helps you choose the right system for your organization’s needs. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they each have distinct scopes and functionalities.
Here's a closer look at each system:
HRIS primarily focuses on storing and managing employee data. It automates core HR functions like payroll, benefits administration, and attendance tracking.
HRMS builds on HRIS by adding more advanced features such as talent management, performance tracking, and recruitment modules. It offers broader tools to manage the employee lifecycle.
HCM is the most comprehensive, encompassing HRMS capabilities plus strategic workforce planning, analytics, learning and development, and employee engagement tools. It supports end-to-end management of human capital aligned with business objectives.
Choosing between these depends on your organization’s size, complexity, and strategic goals. HRIS suits basic HR data management, HRMS fits growing needs with added modules, and HCM is ideal for enterprises seeking integrated, strategic HR solutions.
Now, let's look into the key benefits of implementing an HRIS in your business.
An HRIS offers transformative benefits by automating HR processes, enhancing data accuracy, and improving compliance. It equips organizations with real-time HR analytics, centralized data access, and self-service features that boost employee engagement.
Implementing an HRIS offers numerous advantages that transform how you manage human resources. These advantages simplify operations, reduce risks, and support strategic workforce management.
Adopting an HRIS ultimately supports more agile, data-driven HR management, helping your organization stay competitive and responsive in a dynamic business environment.
Now that we have discussed the benefits of HRIS, let's take a closer look at the specific functions and tasks these systems perform.
Suggested Read: Steps to Create a Fair and Equitable Compensation System
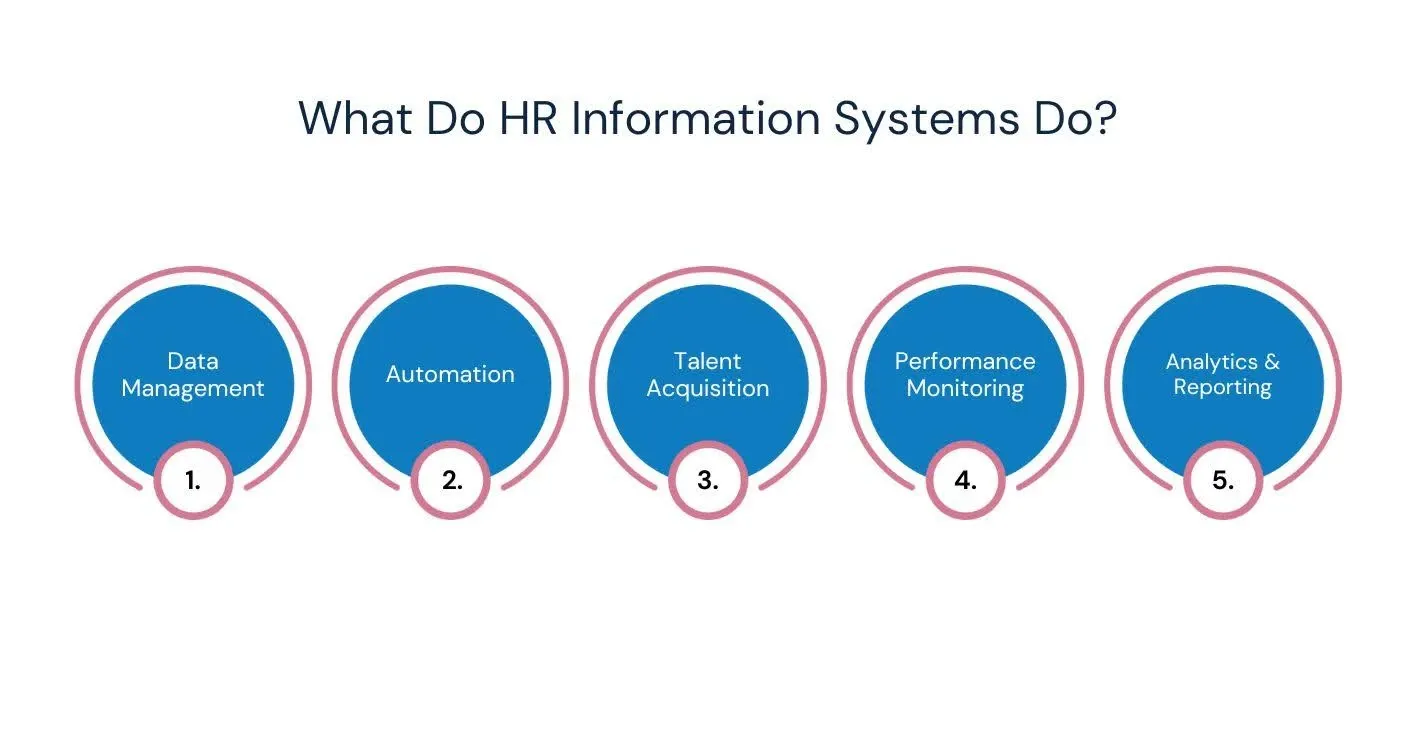
An HRIS centralizes and automates essential HR functions to improve efficiency and accuracy. From managing employee data to supporting recruitment and performance tracking, it streamlines operations and provides valuable insights.
Grasping these capabilities enables you to utilize HRIS effectively for enhancing workforce management and strategic decision-making.
HRIS serves as a centralized database, storing comprehensive employee information, including personal details, employment history, job titles, and compensation data. This organization improves data accuracy, accessibility, and security, enabling HR teams to quickly retrieve and update records while maintaining compliance with regulatory standards.
By automating repetitive tasks like payroll calculations, benefits enrollment, and attendance tracking, HRIS reduces human error and administrative workload. This automation speeds up processes, ensures timely payments and benefits delivery, and frees HR professionals to focus on strategic initiatives rather than manual data entry.
HRIS enhances recruitment through applicant tracking systems (ATS), streamlining the hiring pipeline. It facilitates job posting management, candidate screening, interview scheduling, and onboarding, allowing recruiters to track applicants efficiently and provide a smooth candidate experience from application to hire.
With integrated performance management tools, HRIS enables goal setting, continuous feedback, performance appraisals, and development planning. Managers and employees can work collaboratively to monitor progress, identify strengths, and address areas for improvement. This helps in fueling employee growth aligned with organizational objectives.
HRIS offers solid reporting capabilities and visual dashboards that analyze workforce metrics such as turnover rates, diversity, compliance, and skill gaps. These insights support data-driven decisions, workforce planning, and regulatory compliance, helping organizations anticipate challenges and optimize talent strategies.
Having explored what HRIS systems do, it’s essential to understand the key components that make them effective. These core features work together to simplify HR functions. Let’s take a look at the essential components of an HRIS system.

Suggested Watch: This video will help you understand how HRIS can boost your organizational performance.
Understanding the core components of an HRIS helps you appreciate its full capabilities. These modules work together to automate and manage essential HR functions. Core components of an HRIS integrate essential HR functions into a unified platform. They streamline operations, reduce errors, and enhance workforce management efficiency and effectiveness.
Together, these components support end-to-end human resource management. This integration improves operational efficiency and enhances compliance with regulatory requirements. It also supports strategic workforce planning.

HRIS streamlines performance management by automating appraisals, tracking compensation data, and ensuring pay equity. To understand best practices, CompUp’s webinar, "Deep Dive into Appraisal Season," offers expert insights on navigating merit cycles and compensation trends. Watch it here for actionable strategies.
Now that we have covered the core components of an HRIS, the next step is understanding how to select the right system for your organization.
A well-selected system should help scale with your growth and lead to data-driven HR decisions to optimize workforce management. The buying process is generally not linear. However, these are a few general steps:
The right HRIS turns complicated HR tasks into manageable workflows. Focus on what your organization actually needs, how the system fits technically, and how easy it is to use.
After understanding how to choose an HRIS, it’s important to know when the right time is to implement one. Let’s explore the key indicators that signal it’s time to implement an HRIS in your organization.

From the Community: This thread is for individuals who are new to HRIS and seeking to gain foundational knowledge.
Implementing an HRIS can significantly improve HR operations, but knowing when to make the transition is key. Here are some signs that indicate it might be time to implement an HRIS in your organization.
Choosing to implement an HRIS should be based on clear operational needs rather than trends. When administrative burdens increase or compliance risks grow, an HRIS becomes essential. Now that we have discussed the key steps to consider when selecting an HRIS, it's time to explore the process of implementation.
Suggested Read: Creating a Compensation Job Offer Letter: A Template Guide for Every Situation
Implementing an HRIS is a crucial step in modernizing HR operations and improving efficiency. A well-planned implementation can streamline processes like payroll, recruitment, and employee management.
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you successfully implement an HRIS in your organization.
Ongoing monitoring and optimization after implementing a system will help you continue to adapt and grow with the system as your organization evolves. Now that we have explored the various HRIS systems and their core functionalities, let's examine some real-world examples.
There are several HRIS solutions available in the market, each offering a unique set of features designed to meet the specific needs of organizations. To help you choose the right fit for your business, here are five widely used HRIS software options, each with its own strengths and capabilities:
A cloud-based HR service that supports attendance tracking, shift configuration, and performance management with customizable workflows and a built-in Learning Management System. WorkForce Software uses Zoho People for employee management and time-tracking, while Ola Electric uses it for attendance and employee management.
A comprehensive human capital management (HCM) platform offering employee onboarding, performance management, time tracking, and benefits administration, ideal for larger, remote teams. WeWork uses Sapling HRIS for managing employee onboarding and performance across multiple locations. Uber uses it for onboarding and integrating remote employees globally.
A cloud-based platform that simplifies employee information management, payroll processing, performance appraisals, and leave management to streamline HR tasks. Moderna uses HRM Labs for efficient payroll management and employee performance evaluations in its US offices.
A web-based solution that focuses on payroll processing, benefits administration, talent management, and compliance reporting, making HR processes more automated and efficient. The US branch of HCL Technologies utilizes OptimumHRIS for payroll processing and compliance reporting.
Known for its predictive analytics, IntelliHR uses real-time data across the entire employee lifecycle, offering machine learning models to optimize engagement, productivity, and retention. InterContinental Hotels Group (IHG) uses IntelliHR to collect and analyze employee data for better engagement and productivity.
The five HRIS examples highlighted showcase the diverse solutions available to meet various organizational needs. In the next section, we will address the challenges that organizations may encounter when implementing and managing these systems.
While HRIS systems offer significant benefits, they also present challenges that organizations need to address to ensure their full potential is realized. These challenges can affect everything from data security to user adoption and system integration.
Here are five key challenges that organizations often face when using HRIS systems:
Now that we have covered the key challenges and examples of HRIS, let’s explore how CompUp can simplify the implementation and management of your HRIS.
Implementing and managing an HRIS can be daunting, but CompUp makes the process seamless and efficient. Designed to centralize your HR data, CompUp offers a unified compensation management platform where employee information, payroll, benefits, and performance metrics live in harmony. This reduces data silos and errors, giving you a single source of truth.
These are a few other features that make CompUp exceptional:
CompUp reduces the complexity of HRIS implementation by centralizing data, automating workflows, and providing clear insights. Its customizable features and seamless integrations help you maintain compliance and improve efficiency.
Implementing a Human Resource Information System (HRIS) is a fundamental step toward optimizing HR operations and driving organizational success. A well-structured HRIS simplifies employee data management and automates critical tasks such as payroll processing, benefits administration, and performance tracking.
To unlock the full potential of an HRIS without disruptions, selecting the right system and integration partner is essential. CompUp enhances HRIS functionality by integrating performance ratings from platforms like Lattice, Bamboo HR, and Culture Amp. Companies can use this data for compensation planning and pay equity analysis.
Ready to transform your HR processes and maximize workforce potential? Schedule your free demo today to explore how CompUp can help you improve your compensation strategy.
1. How does the HRIS system work?
An HRIS collects and stores employee data, automates HR tasks like payroll and benefits, and integrates recruitment and performance management. It uses real-time analytics and workflows to streamline processes, improve accuracy, and support strategic HR decisions.
2. What are the five types of HRIS?
The five types are: standalone HRIS (basic data management), modular HRIS (select functions), integrated HRIS (full HR suite), cloud-based HRIS (online access), and enterprise HRIS (large-scale, complex systems). Each fits different organizational sizes and needs.
3. What are the five functions of HRIS?
Key HRIS functions include employee data management, payroll processing, recruitment and onboarding, performance management, and benefits administration. These automate routine tasks, improve data accuracy, and support HR’s strategic workforce planning.
4. What are the four major components of HRIS?
The four major components are employee information systems, payroll management, time and attendance tracking, and benefits administration. Together, they create a comprehensive platform to manage essential HR operations efficiently.

Customer Success Manager - Team Lead
Led by a vision to transform the landscape of total rewards with an innovative mindset and technological advancements.
Revolutionizing Pay Strategies: Don't Miss Our Latest Blogs on Compensation Benchmarking