
Most organizations talk about performance, but few manage it effectively. According to research, only 2 in 10 employees feel their performance is managed in a way that motivates them to excel. This disconnect leads to disengagement, unclear expectations, and stalled growth.
To stay competitive, companies must rethink performance management as a continuous, strategic process. One that drives development, not just documentation. This guide walks you through the essentials to build a performance management system that actually works.
Employee performance management is an ongoing process that helps align individual contributions with organizational goals. It involves setting expectations, monitoring progress, providing feedback, and developing talent over time.
Key aspects of performance management include:
Rather than being a once-a-year review, effective performance management should be ongoing and dynamic. Companies can turn routine check-ins into drivers of productivity and retention by redefining performance management as a strategic partnership.
Next, let us look at why investing in this process pays off.

An effective performance management system creates a structured, supportive environment where individuals can thrive and contribute meaningfully to organizational success. When done right, it inculcates a culture of accountability, growth, and alignment.
Key benefits include:
Now that the benefits are clear, it is essential to understand the foundational structure that supports these outcomes. This brings us to the core components of a performance management system.
Suggested Read: How to Build Pay Structures: Pros and Cons of Salary Bands and Pay Ranges
An effective performance management system is built on a foundation of interconnected components. Each element plays a distinct role in guiding employees, measuring their progress, and ensuring alignment with organizational objectives.
When these parts function cohesively, the result is a fair and future-ready performance ecosystem.
Clear, measurable, and aligned goals provide direction for employees and clarify expectations. These goals should tie directly into team and company-wide objectives to maintain strategic consistency.
Ongoing, two-way feedback allows for real-time improvements and strengthens communication. It helps identify issues early, promote accountability, and reinforce positive behaviors.
Structured performance reviews (quarterly, biannually, or annually) allow managers and employees to evaluate progress, address gaps, and set future priorities. These should be objective, consistent, and based on evidence.
Individual growth plans help employees improve skills, pursue career paths, and address performance issues. This component links performance management with long-term talent development.
Acknowledging high performers through formal and informal rewards strengthens morale and encourages consistent effort. This component supports a culture of appreciation and achievement.
Accurate record-keeping ensures transparency and consistency across evaluations. It also provides valuable data for HR decisions, compliance, and continuous improvement.
These core elements form the building blocks of any performance strategy. But to ensure that these components are driving the right outcomes, organizations must first define their underlying objectives. Let us now examine the goals of performance management.
Suggested Watch: Join industry leaders from Esper.io, Lenskart, and MPL as they unpack real-world compensation strategies during appraisal season. This 96-minute webinar offers practical insights to help you optimize planning, decision-making, and execution.
Effective performance management is about creating a system that allows for continuous improvement, engagement, and alignment. Setting clear goals helps ensure the process is purposeful and outcome-driven, benefiting both the organization and its employees.
Having identified the goals, it becomes important to recognize how these are applied over time. A structured cycle helps organizations implement, monitor, and recalibrate performance efforts. This leads us into the performance management cycle.
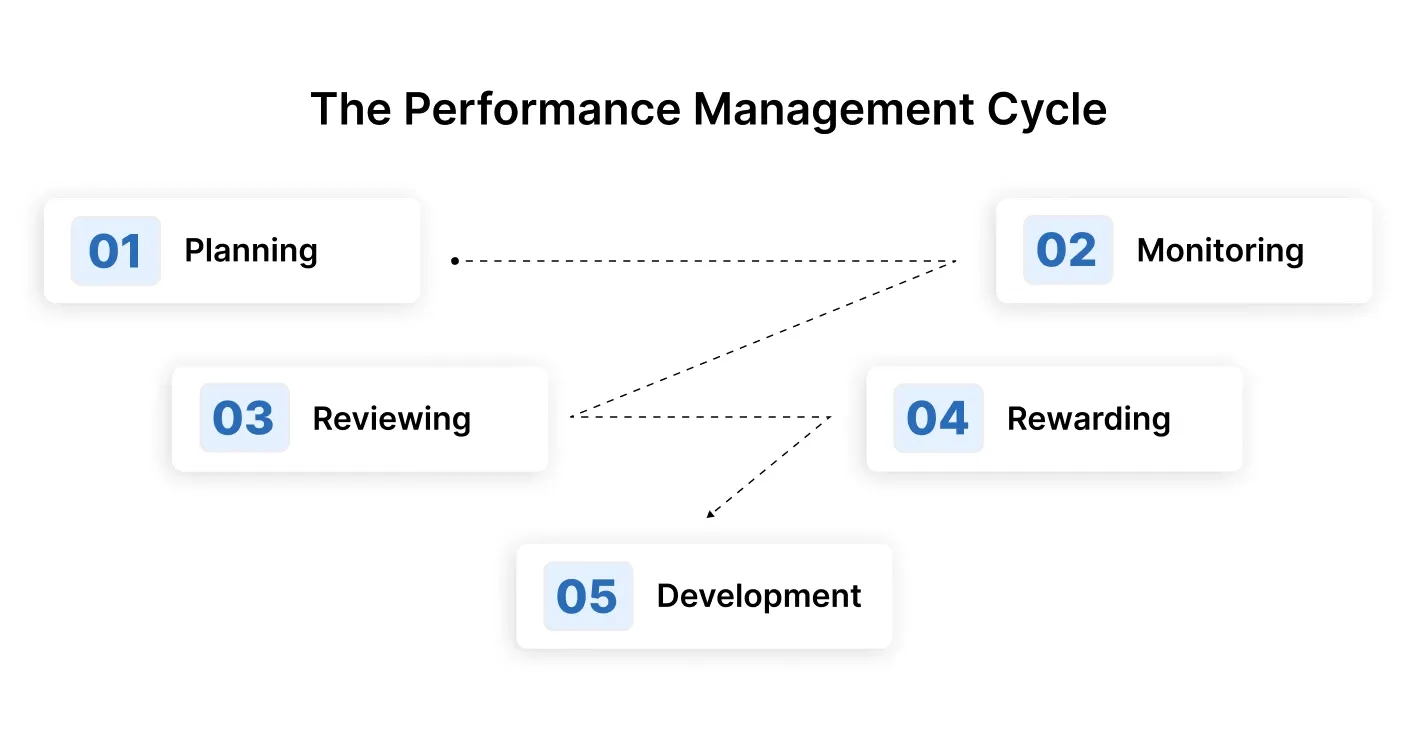
The performance management cycle is a structured, repeatable process that guides how employee performance is planned, monitored, evaluated, and improved. It promotes continuous feedback and alignment throughout the year, helping organizations maintain momentum and accountability.
This phase involves setting clear performance expectations and defining individual objectives that align with team and organizational goals. Managers and employees collaborate to establish measurable outcomes and timelines.
Ongoing observation and real-time feedback are central to this stage. It helps identify challenges early, reinforce positive behavior, and keep employees on track toward their objectives.
Formal evaluations are performed periodically, usually quarterly or annually, to measure performance against set goals. This step provides a structured opportunity to recognize achievements and address areas of improvement.
Recognition, compensation adjustments, promotions, or development opportunities are linked to the outcomes of performance reviews. Fair and meaningful rewards reinforce high performance and promote retention.
Insights gathered from performance reviews are used to create targeted growth plans. Whether through training, mentoring, or role changes, this phase ensures employees continue to grow in alignment with business needs.
Each stage in the cycle plays a vital role in tracking and improving performance. Yet, how this cycle is executed varies depending on the method used. Let us now look at the different methods of performance management that organizations can adopt.
Suggested Read: Building Pay Bands Using Market Reference Points and Benchmark Data
There is no one-size-fits-all method for managing performance. Depending on your organization’s size, structure, and culture, different frameworks may be more effective. The right approach balances structure with flexibility and supports both individual and organizational growth.
This method involves assessing employee performance once a year, typically with a standardized scoring or ranking system. While it provides formal documentation, it can lack agility and timeliness for fast-moving teams.
Continuous performance management replaces the annual review with ongoing conversations. Managers give real-time feedback, promoting immediate course correction and employee development throughout the year.
This method gathers input from an employee’s peers, subordinates, supervisors, and sometimes clients. It provides a more holistic view of performance, particularly useful for leadership development and interpersonal skill evaluation.
MBO focuses on aligning individual objectives with broader business goals. Employees and managers collaboratively set measurable goals, and success is evaluated based on outcomes, not just effort.
Popular in high-growth environments, OKRs set ambitious goals (objectives) supported by measurable actions (key results). They encourage innovation, alignment, and transparency across teams.
This method uses predefined criteria and rating systems to evaluate performance. It works well for roles with clear responsibilities and helps identify skill gaps across the organization.
Each method has its own strengths, but the success of any approach depends heavily on execution. Next, we will walk through the key steps to implement an effective performance management process in your organization.
Suggested Read: How Equity Compensation Works? A Guide for Employees

Implementing a performance management system is more than just setting goals and conducting reviews. It requires building a sustainable structure that supports consistent communication, development, and accountability.
Below are key steps to get your process up and running effectively:
With implementation strategies in place, attention must shift to how managers actively guide and enhance employee performance. Let us now explore actionable strategies for managing employee performance.
The success of your performance management system relies on how leaders engage with employees every day. These five actionable strategies can help managers drive results, retain talent, and cultivate a culture of growth and accountability.
Clarity prevents confusion. Communicate role responsibilities, performance standards, and KPIs clearly from onboarding onward. Ensure every employee understands how their work contributes to broader team and company goals.
Instead of waiting for annual reviews, offer frequent, constructive feedback. Managers should act as coaches by guiding employees, addressing challenges early, and reinforcing positive behaviors regularly.
Recognition motivates. Celebrate both major wins and consistent efforts through verbal praise, incentives, or growth opportunities. Even small gestures can strengthen engagement and morale.
Avoid delay. When performance dips, address it promptly with clarity and empathy. Use performance improvement plans (PIPs), regular check-ins, and mentorship to help employees get back on track.
Empower employees to grow. Provide learning opportunities, stretch assignments, and pathways for advancement. When people see a future with your company, they are more likely to stay committed and perform.
While these strategies can improve outcomes, organizations often face roadblocks that hinder progress. Let us now explore the factors for choosing the right technologies and platforms that support effective performance management.
Modern performance management relies heavily on digital tools that facilitate goal setting, feedback, reviews, and analytics. From enterprise software to lightweight feedback apps, the right technology can simplify complex processes and make performance tracking more consistent and data-driven.
When choosing the right tool for your organization, consider:
An ideal performance management tool supports continuous improvement while reducing administrative overhead.
Leaders can reduce friction by anticipating and addressing everyday challenges. Let us take a closer look at the common challenges in introducing performance management.
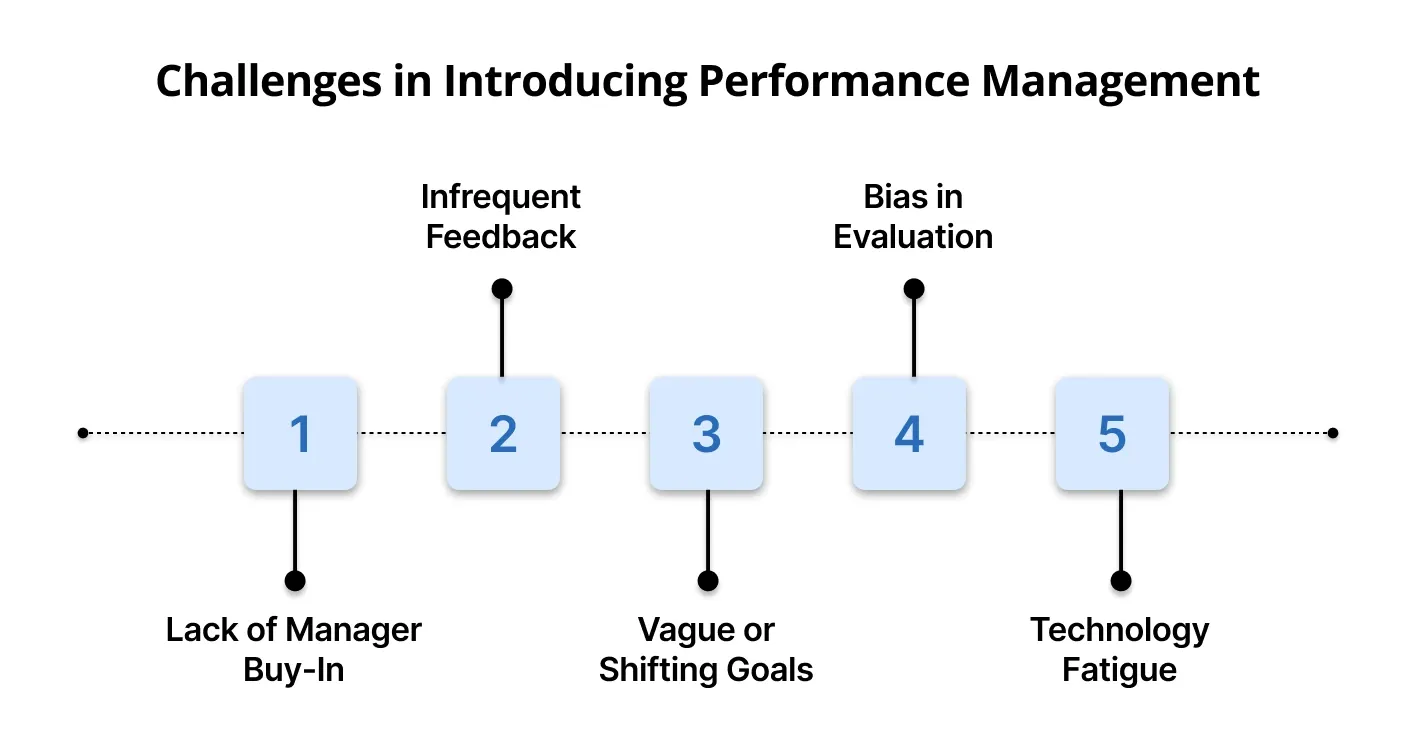
Even the most thoughtfully designed performance management systems can face resistance or falter in execution. Recognizing common hurdles early can help leaders build systems that stick and evolve with the organization’s needs.
If managers view performance management as a formality rather than a leadership tool, they will not use it meaningfully. This can result in inconsistent implementation across teams.
Solution: Train managers on the value of performance conversations and equip them with the skills and tools to lead them effectively. Reinforce accountability through clear expectations and leadership modeling.
Annual reviews alone are inadequate for tracking progress or course correction. Employees feel disconnected when feedback is rare or outdated.
Solution: Embed regular check-ins into team routines and promote a feedback culture where real-time coaching and recognition are the norm.
Unclear or ever-changing objectives leave employees unsure of what success looks like. This misalignment undermines motivation and results.
Solution: Use goal-setting frameworks like OKRs or SMART goals to clarify expectations. Revisit and adjust goals collaboratively when business needs change.
Subjective assessments can lead to perceptions of unfairness, especially when based on personal preferences or inconsistent standards.
Solution: Standardize evaluation criteria and train managers on unconscious bias. Consider adding multi-rater (360-degree) feedback to balance perspectives.
Overly complex tools can hinder adoption and reduce focus on meaningful conversations. When platforms feel burdensome, people disengage.
Solution: Choose intuitive systems that simplify, not complicate, workflows. Involve end-users in platform selection and provide adequate training.
Overcoming these challenges requires thoughtful execution. Fortunately, certain approaches have proven to consistently support successful implementation. Let us now explore the best practices for performance management that organizations should consider.
Implementing a performance management process requires more than just setting up forms or annual reviews. It involves cultural change, leadership support, and clear alignment with organizational goals.
The following best practices can help ensure that your system is both effective and sustainable:
These practices offer a clear path toward stronger performance outcomes. But how do they work in real life? The answer lies in examining corporate examples of performance management done right.
To better understand how performance management works in action, it helps to look at real-world examples. Leading organizations across industries have implemented innovative strategies tailored to their business models, resulting in improved employee engagement, alignment, and outcomes.
Google popularized the use of Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) to drive alignment and accountability across teams.
Adobe replaced traditional annual reviews with a Check-In system focused on ongoing conversations.
GE moved away from its legacy rank-and-yank model to a continuous performance development approach.
Netflix emphasizes a high-performance culture with radical transparency and autonomy.
These organizations show that performance management is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Instead, it evolves with company culture, leadership, and goals. These examples illustrate how theory translates into results.
CompUp checks off on all these and more. This platform offers a comprehensive suite of performance and compensation features designed to align business strategy with employee growth and motivation. Let us take a closer look at how CompUp supports performance management.
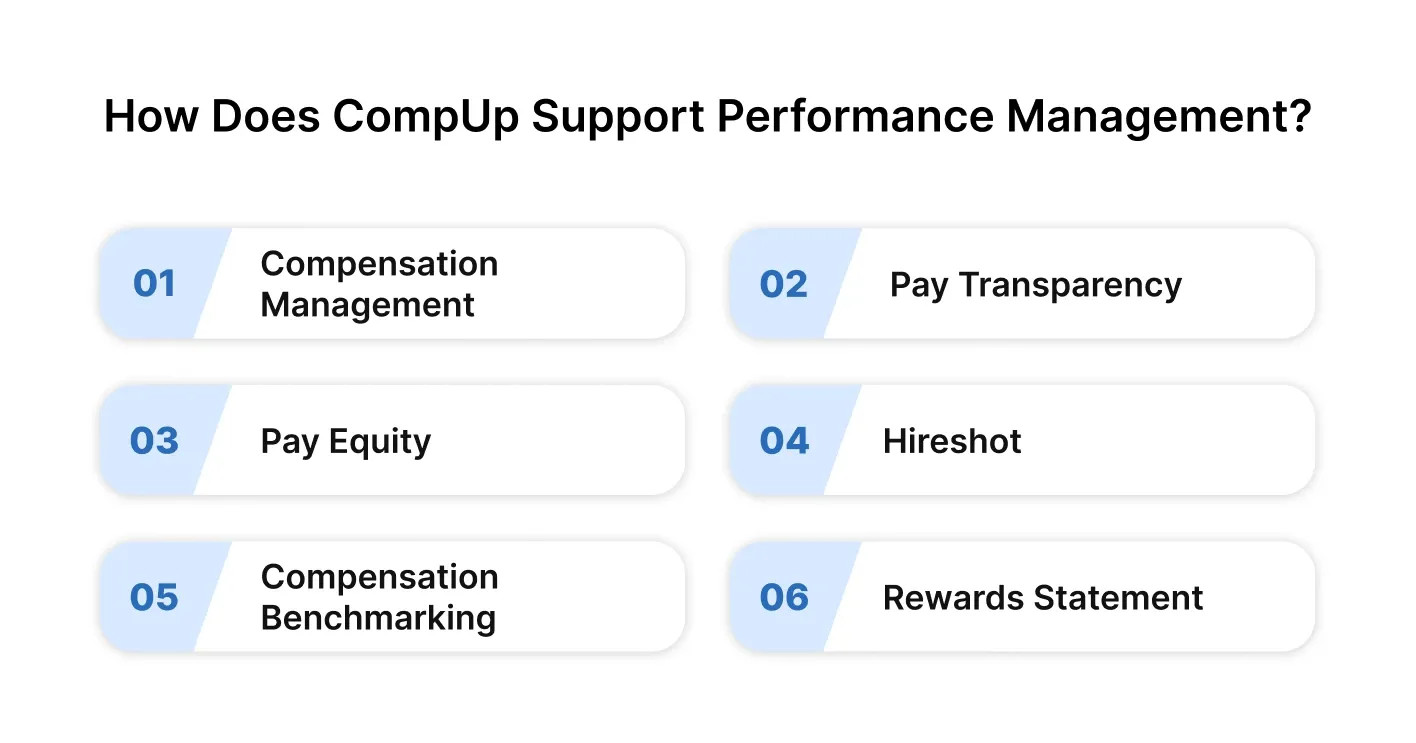
Performance management is most effective when paired with a compensation strategy that rewards progress, encourages transparency, and drives motivation. CompUp unifies performance outcomes with pay decisions, helping organizations link efforts with rewards in a clear, data-driven way.
Below are the core services offered by CompUp and how they support your performance goals:
By integrating performance metrics into annual increments, promotions, and salary adjustments, CompUp ensures that high-performing employees are recognized and rewarded consistently. This alignment creates a culture where performance translates directly into growth and recognition.
Trust is essential for performance to thrive. CompUp enables organizations to communicate compensation structures clearly, helping employees understand how their efforts relate to their pay and advancement. This visibility reinforces accountability and raises employee engagement.
Performance management loses credibility if compensation is not perceived as fair. CompUp identifies and corrects unjustified pay disparities across roles, levels, and demographics, creating an equitable environment where all employees have the same opportunity to succeed based on merit.
CompUp’s Hireshot tools ensure that new hires are brought in with competitive and equitable compensation, along with engaging, informative digital onboarding experiences. This sets performance expectations early and improves retention from day one.
CompUp’s real-time benchmarking tools help HR teams assess market standards and adjust compensation plans accordingly. This ensures that top performers are not just motivated internally, but also retained in a competitive external market.
Motivating long-term performance requires visibility into total compensation and rewards. CompUp gives employees personalized digital access to their complete rewards package, including variable pay, benefits, and future earning potential.
CompUp strengthens performance management by linking employee effort to fair, transparent, and competitive compensation practices. Whether you are planning promotions, engaging new hires, or creating equity, CompUp provides the structure and insights needed to reward performance.
Employee performance management is a continuous, strategic process that aligns individual contributions with organizational success. When done right, it improves morale, encourages growth, and retains top talent through meaningful recognition and development.
CompUp complements this process by offering an intelligent, integrated approach to compensation planning and performance recognition. Beyond its core services, tools like Manager Execution, Digital Onboarding, and the Intelligent Offer Assistant play a crucial role in reinforcing performance-driven cultures.
Ready to turn performance into progress? Get in touch to build a fair, transparent, and high-performing workplace.
1. What are the five elements of performance management?
The five core elements are goal setting, ongoing feedback, performance evaluation, employee development, and recognition. Together, they help align individual efforts with organizational objectives and encourage continuous improvement.
2. What are the 3 C's of performance management?
The three C’s stand for Clarity, Consistency, and Communication. These ensure employees understand expectations, receive regular feedback, and stay aligned with business goals.
3. What is the difference between performance management and performance appraisals?
Performance management is an ongoing process focused on development and alignment. Appraisals are periodic evaluations that assess past performance, typically tied to ratings or compensation decisions.
4. How does HR manage employee performance?
HR supports managers by setting up clear policies, providing performance tools, facilitating feedback systems, conducting training, and ensuring fair evaluations aligned with business strategy.
5. What is continuous performance management?
Continuous performance management replaces annual reviews with regular check-ins, goal updates, and real-time feedback, promoting agility, accountability, and stronger manager-employee relationships.

Customer Success Manager
Driven with the aim of becoming a valuable subject matter expert in the world of Total Rewards to be able to deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Revolutionizing Pay Strategies: Don't Miss Our Latest Blogs on Compensation Benchmarking