
Employee turnover remains a significant challenge for organizations, impacting both financial resources and team dynamics. In 2023, U.S. companies spent nearly $900 billion replacing employees who voluntarily left their positions. This substantial expenditure underscores the importance of understanding the underlying causes of employee departures and implementing effective strategies to mitigate turnover.
This blog examines employee turnover, highlighting its definition, different types, key contributing factors, and the techniques used to calculate turnover rates.
Employee turnover refers to the rate at which employees leave an organization and are replaced. It is typically measured as a percentage of the total number of employees over a specific period. While turnover is a natural occurrence in any organization, a high turnover rate can be problematic, indicating dissatisfaction or systemic issues within the company.
Turnover can impact various aspects of a business, from financial performance to company culture. High turnover can increase recruitment and training costs, disrupt team dynamics, and lower employee morale, while low turnover may indicate a stable and engaged workforce.
Employee turnover can take different forms, each influencing an organization's workforce in distinct ways. Now, let's explore the main types of employee turnover and their impact.
Suggested Read: Understanding What 75th Percentile Means in Salary Compensation

From the Community: Read this Reddit thread to gain more insights into employee turnover
Employee turnover can be classified into different types based on the reasons for departure, the manner in which the departure occurs, and the timing. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for identifying the root causes and addressing them effectively.
Below are the most common types of turnover:
Voluntary turnover occurs when employees choose to leave an organization on their own terms. This may be due to personal reasons, dissatisfaction with their role, better career prospects, or a more attractive compensation package elsewhere. Organizations must analyze voluntary exits to identify workplace issues that impact retention and improve employee satisfaction.
Involuntary turnover happens when an employee is dismissed by the organization due to factors beyond their control. This includes layoffs due to financial constraints, restructuring, or downsizing, as well as terminations due to performance issues or policy violations. Managing involuntary turnover effectively ensures fairness while maintaining operational stability and employee morale.
Functional turnover benefits an organization when underperforming employees leave voluntarily or are let go. When individuals whose skills or work ethic do not align with company goals exit, it allows space for more capable employees to contribute positively. Companies can use functional turnover to refine talent acquisition strategies and enhance overall team effectiveness.
Dysfunctional turnover occurs when high-performing employees exit the organization, negatively impacting operations and morale. Reasons often include inadequate career growth opportunities, lack of recognition, or uncompetitive compensation. Companies should address these concerns proactively by improving engagement, creating growth opportunities, and making top talent feel valued to minimize unwanted departures.
External turnover takes place when employees leave to pursue opportunities outside the organization. This may involve joining competitors, switching industries, or starting personal ventures. Organizations can mitigate external turnover risks by offering strong career development paths, competitive compensation, and a workplace culture that encourages long-term commitment and professional growth.
Retirement turnover occurs when employees leave an organization due to attaining retirement age or choosing early retirement. While it is a natural part of workforce planning, businesses must implement succession strategies and knowledge transfer processes to ensure continuity. Proper planning helps maintain institutional knowledge, minimize disruptions, and facilitate a smooth transition for new employees.
Understanding the different types of employee turnover is just the first step. To effectively reduce turnover, organizations must recognize the underlying causes that drive employees to leave. Now, let's explore the key reasons behind employee turnover.
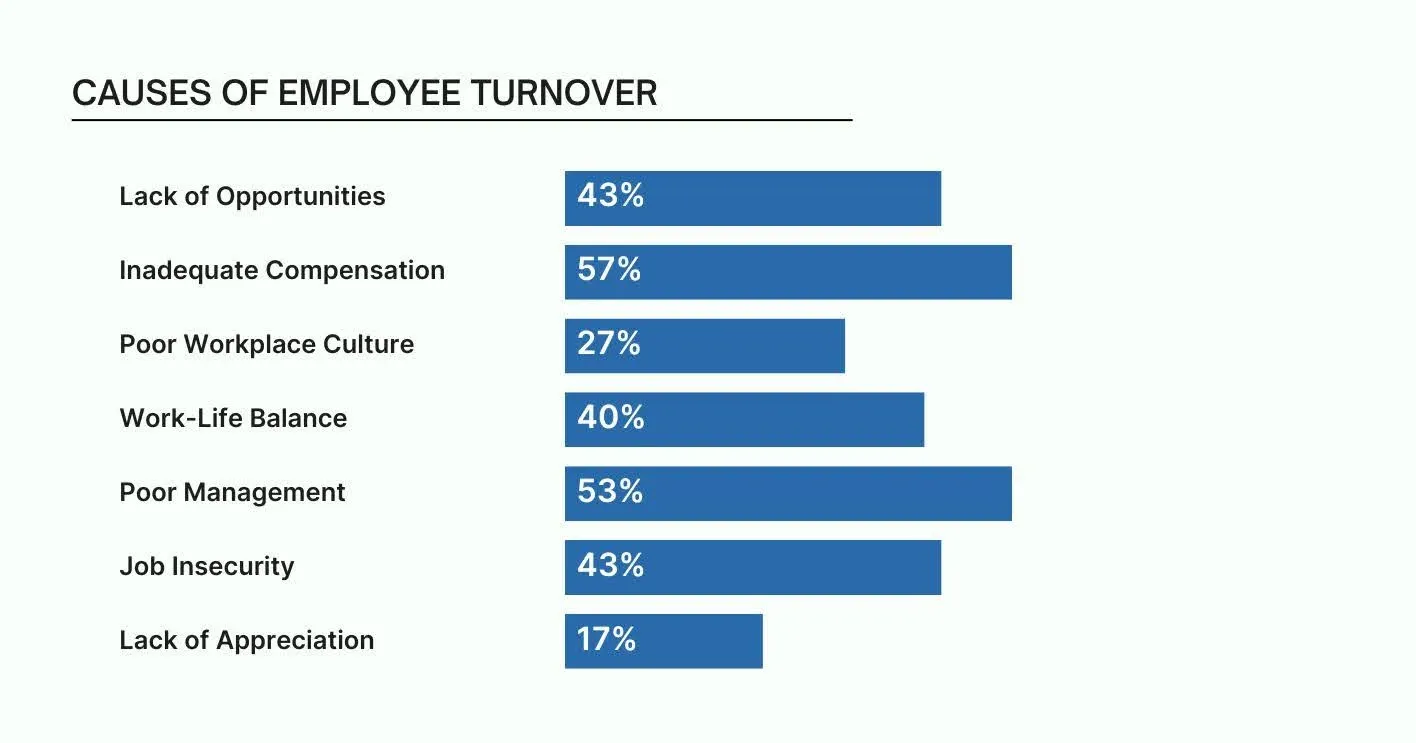
Employee turnover can occur for a variety of reasons, ranging from dissatisfaction with compensation to issues with management or the work environment. Understanding the root causes of turnover is critical for businesses to reduce attrition rates and enhance employee retention. Below are some of the primary causes:
Employees who feel their careers are stagnating are more likely to seek new opportunities. A lack of professional development, limited promotion paths, or stagnant skill growth can lead to disengagement and increased turnover. Career advancement is one of the most common motivators for changing jobs.
Employees who feel their compensation is not competitive or equitable compared to industry standards may leave for better-paying opportunities. Besides salary, it also includes benefits like healthcare, retirement plans, and bonuses. Organizations with poorly structured or inadequate benefit packages may face higher turnover.
An organization's culture plays a significant role in employee satisfaction and retention. A toxic work environment, poor communication, or a lack of alignment with company values can drive employees away. If employees don’t feel valued or supported by management, they are more likely to leave.
Improving workplace culture requires strong leadership, open communication, recognizing employee achievements, and promoting inclusivity. Developing a positive, collaborative environment is key to employee satisfaction.
The inability to maintain a healthy work-life balance is a significant contributor to turnover, especially in high-pressure industries. Employees who feel overworked or unable to balance their personal and professional lives may experience burnout, leading to higher turnover rates.
Ineffective or unapproachable management is one of the leading causes of employee turnover. Employees who feel unsupported, micromanaged, or unappreciated by their managers are more likely to leave. Poor communication, lack of feedback, or failure to recognize employees’ contributions can undermine job satisfaction.
Employees in organizations experiencing financial instability or frequent layoffs often face job insecurity, leading to higher turnover. In uncertain times, employees seek more stable opportunities to ensure their job security.
Employees who feel undervalued or unrecognized for their efforts are more likely to look for other opportunities. Regular recognition and appreciation play a vital role in employee retention, as they foster a sense of worth and motivation.
Organizations should implement employee recognition programs, reward high performance, and celebrate achievements. Whether through financial incentives, public acknowledgment, or career advancement, making employees feel appreciated is crucial for reducing turnover.
Next, let's examine the key consequences of high turnover and how businesses can mitigate its impact.
Suggested Read: Understanding How an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOP) Works

Suggested Watch: This video defines what employee turnover is, what the root causes are, and how you can lower it at your organization.
High employee turnover can disrupt business operations, increase costs, and weaken workplace morale. When employees leave frequently, organizations struggle with productivity, retention, and long-term stability. Understanding the effects of turnover allows businesses to develop effective strategies that reduce disruptions and promote a more engaged workforce.
CompUp’s predictive analytics can help prevent challenges in workforce planning. The compensation management platform can anticipate workforce changes, optimize hiring plans, and align talent strategies with long-term objectives to ensure stability and efficiency.
To mitigate these consequences, businesses must focus on employee engagement, career development, competitive compensation, and a positive work environment. Strengthening retention strategies ensures workforce stability and long-term organizational success. These are explained in greater detail in the next section.
Reducing employee turnover requires a proactive approach focused on engagement, career growth, fair compensation, and a supportive workplace culture. Here are key strategies to help organizations improve retention and build a committed workforce.
Engaged employees are more likely to stay long-term and contribute meaningfully to the organization. Companies should create a culture of open communication, regular feedback, and active participation. Encouraging collaboration, recognizing achievements, and creating a strong sense of purpose can significantly boost employee satisfaction.
Lack of career growth is a common reason employees seek new opportunities. Organizations must offer training programs, mentorship initiatives, and internal mobility options. By investing in professional development, businesses empower employees to advance their careers while remaining within the company.
Fair and transparent compensation plays a crucial role in retention. Employers should conduct regular salary benchmarking, provide performance-based incentives, and offer meaningful benefits such as health coverage, retirement plans, and wellness programs. CompUp’s predictive analytics, businesses can optimize compensation strategies to align with industry standards and employee expectations.
Monitoring workplace sentiment helps organizations detect emerging issues before they escalate. AI-driven employee sentiment analysis allows HR teams to track employee feedback trends and take timely action to resolve concerns. Regular check-ins, anonymous surveys, and open-door policies ensure employees feel heard and supported.
Effective leadership significantly impacts employee retention. Managers should instill trust, provide mentorship, and create a growth-oriented environment. Training leadership teams to support employees, offer constructive feedback, and encourage professional development enhances long-term workforce stability.
Implementing these strategies helps businesses build a resilient workforce, reduce turnover, and maintain a thriving organizational culture. A combination of engagement, career growth, fair compensation, and proactive workforce planning ensures long-term success.
Now that we have covered key strategies to reduce turnover, let's take a closer look at how to calculate employee turnover rates and track workforce stability.
Understanding how to calculate turnover rate is essential for evaluating workforce stability and identifying areas for improvement in retention strategies.
The turnover rate represents the percentage of employees who leave an organization during a specific time period, relative to the average number of employees during that period.
The basic formula to calculate turnover rate is:
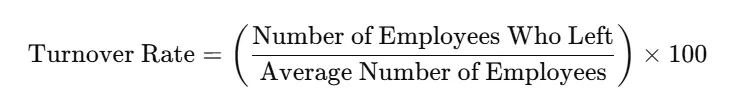
Where:
Calculating employee turnover is essential for understanding workforce stability and identifying potential issues. To accurately calculate turnover, you need to gather key data, including the number of employees who left and the average headcount during a specific time period.
Steps for calculating employee turnover are:
This process helps businesses track trends, assess retention strategies, and make informed decisions. The turnover rate provides valuable insight into organizational health and the effectiveness of HR practices.
Let’s assume a company had 100 employees at the start of the year and 90 employees at the end of the year. During this period, 15 employees left the company.
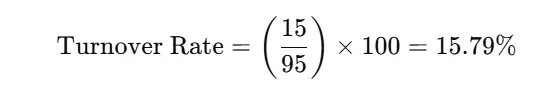
In this example, the annual turnover rate is 15.79%.
Employee turnover comes with significant costs that go beyond replacing a departing worker. High turnover can strain an organization’s resources and stability. Understanding these financial, human, and brand implications is essential for businesses aiming to strengthen retention and minimize disruptions.
A high turnover rate could indicate dissatisfaction or poor organizational culture, while a low turnover rate may signal high employee engagement and satisfaction. This brings us to the next section on identifying a healthy employee turnover rate.
A healthy employee turnover rate strikes the right balance between business needs and workforce retention, ensuring sustainable employee departures without disrupting performance, morale, or long-term stability.
Why is this important? According to Gallup, U.S. businesses spend $1 trillion annually replacing employees who voluntarily leave. Managing turnover effectively minimizes these costs and strengthens workforce continuity.
So, what does a healthy turnover rate look like? The Society for Human Resource Management’s (SHRM) Human Capital Benchmarking database reports that the annual turnover rate averages 15% across industries, serving as a useful benchmark for organizations assessing their retention strategies.
These are the guidelines for a healthy turnover rate:
Employee turnover rates vary across industries, influencing workforce stability and business operations. The table below presents separation rates for different sectors, highlighting industries with the highest and lowest turnover.
Leisure & Hospitality:
Transportation:
Professional Services:
Mining & Logging:
Retail Trade:
Other Sectors:
Construction:
Overall Workforce:
Education:
Real Estate:
Healthcare:
Manufacturing:
Information Services:
Wholesale Trade:
Finance & Insurance:
Government:
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics
A healthy employee turnover rate is vital for sustaining workforce efficiency without disrupting operations. CompUp delivers compensation benchmarking, which helps organizations optimize salary structures to stay competitive and reduce voluntary attrition. Aligning pay strategies with industry standards makes sure that the employees feel valued and motivated to stay.
Now, let’s explore how it minimizes employee turnover.
Suggested Read: Defining DEIB: Understanding Diversity, Equity, Inclusion, and Belonging at Work
CompUp offers an integrated platform designed to streamline key HR processes, making it easier for organizations to reduce employee turnover. By focusing on employee engagement, career development, performance management, and compliance, CompUp helps businesses address the root causes of turnover efficiently.
Here’s how CompUp supports retention efforts:
CompUp provides tools that allow employees to provide regular feedback and engage with management. Predictive analytics can detect early signs of disengagement by analyzing employee feedback trends. Organizations can proactively address concerns, reducing turnover risks before they escalate.
CompUp facilitates continuous performance tracking with goal-setting and feedback tools, ensuring employees stay aligned with business objectives. Rewarding achievements inculcates a culture of appreciation and long-term commitment. Market insights allow businesses to align performance goals with industry standards.
CompUp streamlines payroll and benefits administration, enhancing transparency in compensation. Easy access to benefits information improves employee satisfaction, reducing turnover linked to pay-related concerns. The tool helps with pay equity by analyzing compensation structures and identifying disparities. Fair and transparent pay strengthens employee trust, reducing turnover caused by wage dissatisfaction.
With flexible scheduling and leave management tools, CompUp helps employees maintain a healthy work-life balance. Reducing burnout leads to higher retention and improved workplace morale. Through pay transparency, CompUp empowers employees with clear insights into compensation and benefits. Transparency paves the way for fairness, improving work-life balance and overall job satisfaction.
CompUp optimizes workforce planning by forecasting turnover risks and aligning onboarding efforts with business needs. A structured onboarding experience enhances retention from day one. The tool helps businesses accelerate the integration of new hires into the workplace.
CompUp equips organizations with a powerful suite of tools designed to address the root causes of employee turnover. It enhances workplace culture with real-time feedback, performance tracking, and flexible work solutions. This is useful in reducing burnout and improving employee satisfaction.
Understanding employee turnover is essential for building a stable, engaged workforce. High turnover can lead to increased costs, loss of knowledge, and operational disruptions, while low turnover may signal disengagement or stagnation. Identifying the causes allows organizations to implement targeted strategies that enhance employee satisfaction and retention.
Struggling with high turnover or inefficient workforce management? Let CompUp's experts help. Schedule a demo with our team to assess your needs and learn how our solutions can address your unique challenges.
1. What are the main causes of employee turnover?
The main causes of turnover include poor management, lack of career growth opportunities, inadequate compensation, poor work-life balance, and negative workplace culture. External factors like economic conditions can also contribute to employees seeking new opportunities.
2. What is the root cause of turnover?
The root cause of turnover typically lies in employee dissatisfaction with management, lack of career progression, low compensation, or a negative work environment. Addressing these issues through feedback and improvement strategies can significantly reduce turnover rates.
3. How do you explain employee turnover?
Employee turnover occurs when employees leave an organization voluntarily or involuntarily. It can be influenced by job dissatisfaction, lack of advancement, or external opportunities. High turnover rates often signal organizational problems that need attention to improve employee retention.
4. What does high turnover say about a company?
High turnover can indicate systemic issues within the organization, such as poor management, lack of engagement, inadequate compensation, or an unhealthy work culture. It highlights the need for strategic changes in HR practices to improve employee satisfaction and retention.
5. How can CompUp help reduce employee turnover?
CompUp reduces turnover with predictive analytics to identify risks, real-time feedback to address concerns, performance management to align goals, pay transparency to ensure fairness, and work-life balance tools to improve satisfaction.
6. What features of CompUp support employee retention?
CompUp enhances retention with pay transparency for fair compensation, performance tracking to align employee goals, and work-life balance solutions like flexible scheduling. This helps businesses create a stable, engaged, and motivated workforce.

Customer Success Manager - Team Lead
Led by a vision to transform the landscape of total rewards with an innovative mindset and technological advancements.
Revolutionizing Pay Strategies: Don't Miss Our Latest Blogs on Compensation Benchmarking