
In recent years, pay transparency has become a critical topic in the workplace. States across the U.S. are implementing new laws to ensure equal pay and reduce wage disparities. According to a 2023 study by the National Women's Law Center, the gender pay gap still stands at 81 cents for every dollar earned by men.
This gap is even wider for women of color, with Black women earning just 63 cents and Latina women earning 54 cents for every dollar earned by white men. These disparities highlight the urgent need for more transparency in compensation practices.
The push for pay transparency is gaining momentum. Multiple states now enforce laws requiring employers to disclose salary ranges in job postings or during hiring processes. Yet, for businesses, navigating these evolving laws can be overwhelming. Each state implements its own set of pay transparency requirements, so HR teams must stay informed to ensure compliance. Failing to do so can not only lead to legal consequences but also damage employee trust and morale.
In this guide, we will examine the key components of pay transparency laws in different states and their impact on business practices. The article will also explain how HR professionals can stay compliant while promoting fair pay in their organizations.
Pay transparency laws are designed to ensure fairness and reduce compensation disparities across genders, races, and other demographics. While each state has its regulations, several core elements are common to all laws.
Here are the key components of pay transparency laws that employers should be aware of:
Many states require employers to disclose salary ranges for open positions either in job postings or during the hiring process. This transparency helps level the playing field, allowing candidates to make informed decisions and reducing potential pay discrimination. Some states, like Colorado and California, mandate that employers provide salary information to applicants upon request, ensuring that employees and candidates are aware of the compensation range for the role.
Several states have banned employers from asking about a candidate’s past salary. This aims to prevent the perpetuation of existing pay disparities, particularly among women and minority groups, who may have historically been underpaid. By focusing on skills and qualifications, employers can offer salaries based on the job’s market value, not on past pay rates.
Employers are increasingly required to publicly post wage ranges for job positions. This ensures that compensation is visible, giving candidates an idea of what they can expect and what the employer is willing to pay. In states like New York, companies must include the salary range in job advertisements, promoting greater pay equity and reducing hidden wage gaps.
Employees are often hesitant to discuss their pay for fear of retaliation. Pay transparency laws provide protections for employees who choose to share salary information with others, ensuring they won’t face any negative repercussions. This safeguard promotes a culture of openness, where employees feel empowered to discuss compensation without fear of job loss, demotion, or any other forms of retaliation.
Some states, such as California, have implemented pay data reporting requirements, compelling employers to submit information about their workforce’s pay by gender, race, and job category. This helps regulators and employers track pay gaps and work towards achieving pay equity within the workplace. Employers are required to keep these records to ensure transparency and support any regulatory efforts to investigate potential pay disparities.
Suggested Read: Explore the different types of compensation management, from salary to bonuses, and learn how to structure pay plans that attract and retain top talent.
As pay transparency gains traction, states across the U.S. are implementing new regulations to ensure equal pay and fairness in the workplace. While these laws vary, they share a common goal: eliminating pay disparities and promoting greater transparency.
In the next section, we will examine specific pay transparency laws by state, highlighting key provisions and their effective dates.
Pay transparency laws have become a focal point for many states across the U.S. These laws are designed to promote equity, reduce wage disparities, and ensure that compensation practices are open and consistent. Businesses must understand and comply with these evolving requirements.
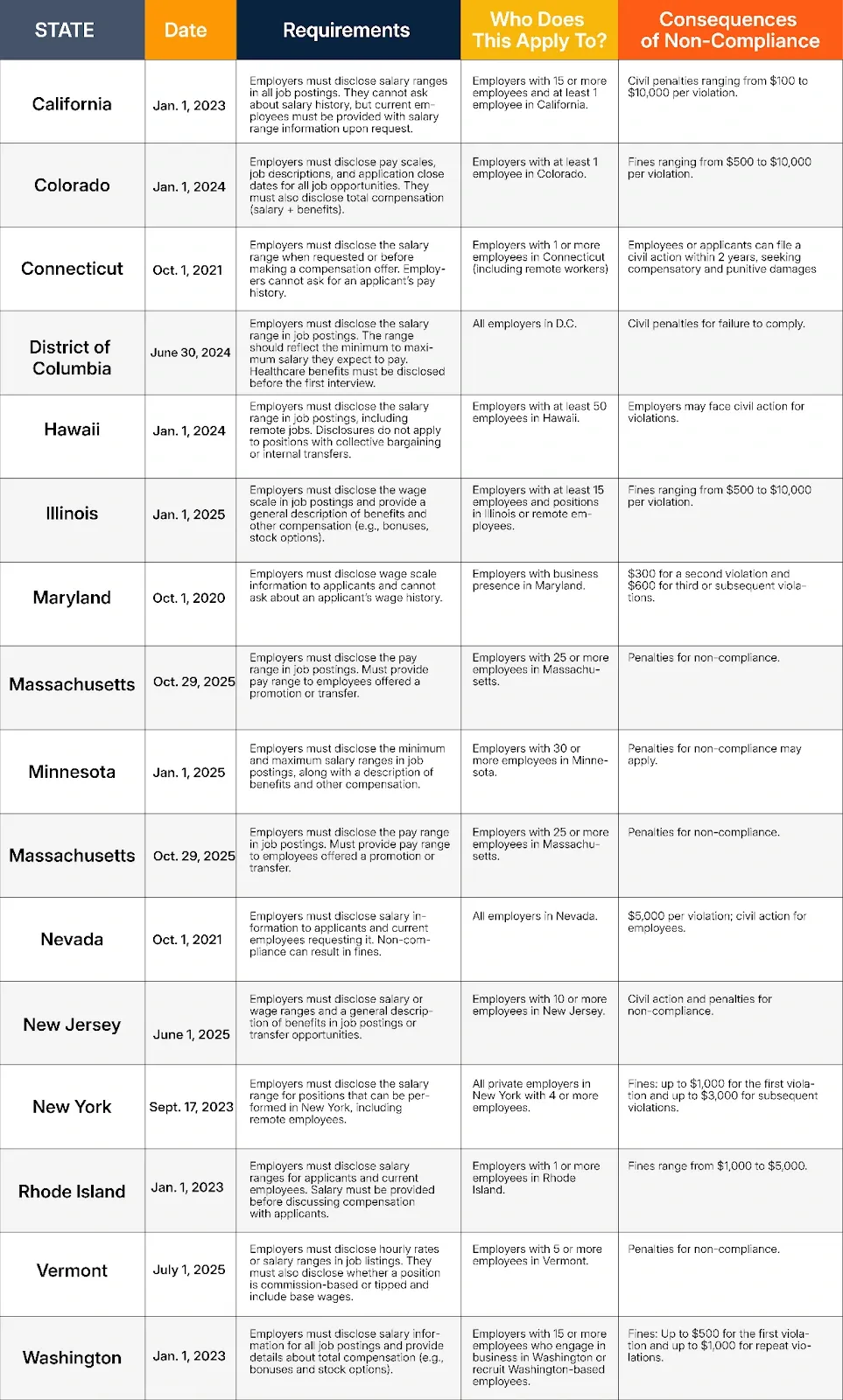
Let’s examine these laws more closely and see how they are shaping the future of pay equity across the country.
California's pay transparency law, effective January 1, 2023, requires employers to disclose salary ranges in all job postings. Employers are prohibited from asking applicants about their salary history, ensuring that new compensation offers are based on the job and qualifications, not prior pay.
Additionally, employers must provide salary range information to current employees upon request. For remote employees, salary information must also be included in job postings for positions that can be performed remotely. Employers with at least one employee in California are obligated to disclose salary ranges to their current employees upon request.
Companies with at least 15 employees must comply with all aspects of this law. Non-compliance can result in civil penalties ranging from $100 to $10,000 per violation, emphasizing the importance of adhering to the law’s requirements.
Colorado’s Equal Pay for Equal Work Act, initially enacted in 2021, was updated in 2023 to further promote pay transparency. Effective January 1, 2024, the law requires employers to post, advertise, and notify employees of all job opportunities, including promotions, and disclose pay scales, job descriptions, and the application window close date in all job listings.
However, this requirement does not apply to jobs that will be performed entirely outside Colorado or postings published outside the state.
The law also mandates that total compensation, including salary, benefits, bonuses, and commissions, be disclosed. Employers with at least one employee in Colorado must comply, and failure to do so can result in fines ranging from $500 to $10,000 per violation. These changes aim to enhance equity and transparency in compensation practices.
Connecticut’s pay transparency law, effective October 1, 2021, requires employers to disclose the salary range for a position during the hiring process in the earliest of the following situations: when the applicant requests it or prior to or at the time the applicant is made an offer of compensation.
Employers must also provide salary information to current employees upon request or whenever they change positions. Additionally, employers may not ask about an applicant’s pay history unless the applicant voluntarily discloses it.
This law applies to all employers with at least one employee in Connecticut. Employees or job applicants can file a civil action against employers who violate the law within two years of the violation, seeking compensatory and punitive damages, along with costs.
The District of Columbia’s pay transparency law, effective June 30, 2024, requires all employers, regardless of size, to disclose salary information in job listings. Employers must provide the minimum and maximum projected salary or hourly pay in all job postings and position descriptions.
Employers are required to state the salary range from the lowest to the highest salary they reasonably expect to pay for the advertised job, promotion, or transfer opportunity at the time of the posting.
Additionally, employers must disclose to prospective employees the existence of healthcare benefits available to them before the first interview.
Hawaii’s pay transparency law, effective January 1, 2024, requires employers to include a salary range or hourly wage rate in job postings. The description should accurately reflect what the employer wants to pay for the position. This law applies to employers with at least 50 employees.
However, it excludes certain situations, including public employee positions where compensation is determined under a collective bargaining agreement and internal transfers or promotions.
Employers who violate this law may face civil action from employees or applicants, allowing them to seek compensatory and punitive damages and costs.
Illinois' pay transparency law, effective January 1, 2025, mandates that employers must include the wage scale they reasonably expect to pay for a position in the job posting. In addition to salary information, employers must also provide a general description of any benefits included in the total compensation package, such as bonuses, stock options, and other incentives.
This law applies to any position that will be physically performed in Illinois or positions performed outside of Illinois but where the employee reports to a supervisor, office, or work site in Illinois. It also applies to employers with at least 15 employees.
Non-compliance can result in fines ranging from $500 to $10,000 per violation. This law aims to promote pay transparency and equity by ensuring candidates have a clear understanding of compensation packages from the outset.
Maryland's pay transparency law, effective October 1, 2020, requires employers to provide wage scale information to job applicants upon request. Employers are also prohibited from requesting an applicant's wage history, ensuring that compensation decisions are based on the job and qualifications rather than past earnings.
This law applies to all employers engaged in business in the state of Maryland.
The law encourages fair pay practices and transparency, helping to reduce wage disparities in the hiring process. Non-compliance can result in a warning for the first violation, a $300 fine for the second violation, and a $600 fine for the third or subsequent violation.
Starting October 29, 2025, Massachusetts employers with 25 or more employees will be required to disclose the pay range for a position in any job posting or advertisement. Employers must also provide the pay range to employees who are offered a promotion or transferred to a new position with different responsibilities.
Additionally, employers must disclose the pay range for a position to an employee currently in that position or to any applicant requesting it.
The pay range is defined as the annual salary range or hourly wage range that the employer reasonably and in good faith expects to pay for the position at the time of the posting.
Recommended Read: Dive into the crucial distinctions between pay equity and pay equality and learn how each impacts compensation strategies and workplace fairness.
Starting January 1, 2025, Minnesota employers with 30 or more employees will be required to disclose the minimum and maximum annual salary range or hourly wage range for positions in all job postings.
Employers must base the range on their good faith estimate and cannot leave it open-ended. Additionally, employers must provide a general description of benefits and other compensation, including health and retirement benefits, offered for the position.
This requirement applies to any job posting, whether made electronically or in print, that outlines desired qualifications for a position intended to recruit applicants. This includes job postings made by recruiters or other third-party entities on behalf of the employer.
Nevada's pay transparency law, effective October 1, 2021, mandates that employers must provide salary information to applicants for any role they interview for. This law applies to all employers in Nevada.
Employers must also disclose salary information to current employees who are seeking a promotion or internal transfer if they request it and one of the following conditions is true:
Employees and job seekers have the right to bring civil action against employers for violations. The Labor Commission may impose fines of $5,000 per violation and cover investigation and attorney costs.
Effective June 1, 2025, employers in New Jersey with 10 or more employees over 20 calendar weeks who conduct business, employ individuals or take applications for employment within the state must disclose specific compensation details in all internal or external job postings or transfer opportunities.
These employers are required to disclose:
Additionally, in Jersey City, employers with five or more employees must disclose a minimum and maximum salary and/or hourly wage, including benefits, in any print or digital media circulating within the city when providing notice of employment opportunities.
New York’s pay transparency law, effective September 17, 2023, mandates that employers must disclose salary ranges for positions that can or will be performed in New York. The law also applies to remote employees whose jobs can be performed outside of New York but who report to a supervisor, office, or work site in New York.
Employers found in violation of this law can face fines:
This law applies to all private employers in New York with four or more employees.
Rhode Island's pay transparency law, effective January 1, 2023, requires employers to disclose salary ranges for job applicants and current employees if requested. For job applicants, salary information must be provided before discussing an offer of compensation.
Current employees must disclose their salary range at the time of hire or before they move to a new position. Additionally, employers are prohibited from seeking the wage history of any applicant. This law applies to employers with at least one employee in Rhode Island.
Depending on the violation, non-compliance with this law can result in fines of $1,000 to $5,000.
Effective July 1, 2025, Vermont employers with five or more employees must disclose hourly rates or salary ranges in job listings that reasonably reflect the actual expected compensation for the position.
Employers must also take the following specific actions for job openings:
This requirement applies to both external job postings and internal transfers or promotions within a current employer.
Washington’s pay transparency law, effective January 1, 2023, mandates that all job postings must include salary information. For internal job transfers and promotions, employers must disclose salary ranges at the employee's request. Additionally, job postings must include a general description of benefits and information about any other compensation, such as bonuses, stock options, and commissions.
This law applies to employers with 15 or more employees who engage in business in Washington or recruit for positions that Washington-based employees could fill.
Employers who violate the law may be ordered to pay damages to employees and 1% interest per month. Fines for violations range from $500 for a first offense to $1,000 or 10% of damages for repeat violations, plus additional fees, interest, and costs.
Navigating pay transparency laws can be complex, especially with the differences across states and local jurisdictions. However, by staying informed and adapting business practices accordingly, employers can foster a more transparent and equitable work environment.
Staying ahead of these legislative changes can help businesses create competitive compensation strategies that attract top talent while maintaining compliance.
As pay transparency laws become more widespread, ensuring compliance across different states can be complex and time-consuming for HR teams. CompUp, a cutting-edge compensation management platform, helps organizations stay ahead of changing regulations by providing real-time insights into salary structures.
It ensures that job postings, offers, and internal promotions adhere to the required salary disclosure rules. With CompUp, employers can:
CompUp empowers HR teams to easily navigate the evolving landscape of pay transparency laws, mitigating risks and building a more transparent, equitable workplace.
As pay transparency laws continue to evolve across the United States, employers must stay informed and compliant. This is necessary to avoid legal risks and foster a fair, equitable work environment.
With regulations in place or on the horizon in many states, understanding the specific requirements for salary disclosures is crucial. This includes compensation structures and employee benefits. Navigating the complex landscape of pay equity is essential for compliance.
Employers who adapt to these changes and use the right tools stay compliant. They also enhance their reputation and attract top talent. Most importantly, they foster a more inclusive and transparent workplace.
Make sure your organization is prepared for the future of pay transparency. CompUp is here to help you every step of the way. Schedule your demo today.
Do I need to update job postings frequently to meet pay transparency laws?
Yes, employers need to update job postings to include salary ranges, especially in states with active pay transparency laws. With CompUp, job postings are automatically updated with salary range disclosures to ensure that they meet the required standards. This saves HR teams time and reduces the risk of non-compliance.
Can CompUp help with tracking compensation across different states with varying pay transparency laws?
Yes, CompUp tracks the latest pay transparency laws across different states. It provides state-specific compliance alerts so HR teams are always aware of updates or new laws that may impact salary disclosures. This ensures employers can stay compliant no matter where they operate.
How can CompUp assist with internal pay equity and salary audits?
CompUp helps businesses identify pay disparities and salary compression issues by offering compensation analytics and insights. HR teams can easily track compensation across departments and job levels, ensuring that salary structures align with pay equity goals and adhere to transparency standards.
Can CompUp automate salary range disclosures for remote positions?
Yes! CompUp automatically includes salary information in job postings for remote positions. It ensures that remote workers receive the same pay transparency benefits, whether they’re located in the same state as the employer or elsewhere. This helps employers stay compliant with regulations, regardless of where their employees work.

Co-founder & CEO, CompUp
Anurag Dixit, founder of CompUp, is a seasoned expert in all things compensation and total rewards. With a deep understanding of the current compensation trends, his vision is to help companies create fair, transparent, and effective compensation strategies.
Revolutionizing Pay Strategies: Don't Miss Our Latest Blogs on Compensation Benchmarking